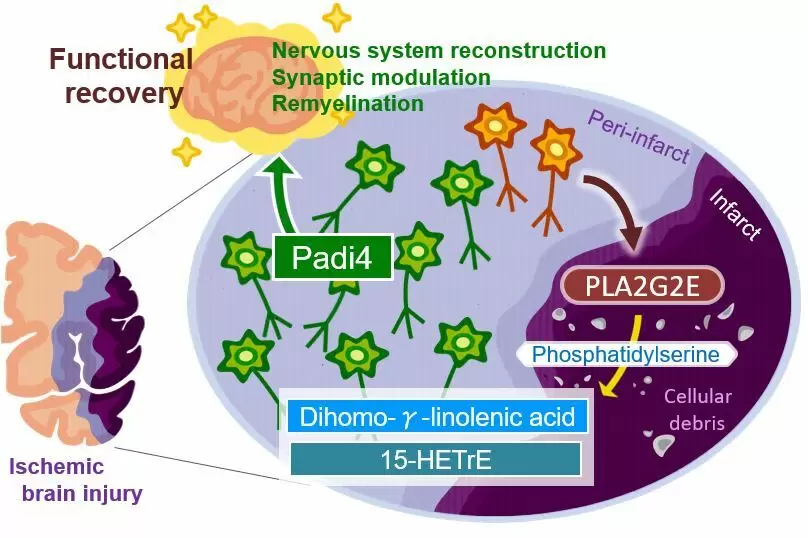
The neurons around an injured brain region will play major roles in promoting functional recovery through nervous system development, synapse organization, and remyelination; however, the molecular mechanisms triggering such a broad range of neural repair after brain injury remained unknown. Our study demonstrated that the secretion of PLA2G2E from perilesional neurons with ischemic stress generated DGLA and 15-HETrE, which triggered these recovery processes through the neuronal Padi4-dependent induction of cluster formation associated with neural repair after ischemic brain injury.
Partial recovery after ischemic stroke is possible, but the mechanisms involved in this process remain unclear. Researchers identified a whole new pathway promoting brain repair. They discovered lipids secreted from neurons surrounding the area of cell death can trigger brain-autonomous neural epair after ischemic brain injury. These findings might contribute to developing new compounds to stimulate the brain’s intrinsic repair mechanisms.
Patients often experience functional decline after an ischemic stroke, especially due to the brain’s resistance to regenerate after damage. Yet, there is still potential for recovery as surviving neurons can activate repair mechanisms to limit and even reverse the damage caused by the stroke. How is it triggered though?
In a study published recently in Neuron, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) provided new insights regarding this question by identifying a new mechanism. They discovered that neurons surrounding the area of cell death secrete lipids that can trigger brain-autonomous neural repair after ischemic brain injury.
An ischemic stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is blocked and results in the death of brain cells. This condition is life-threatening, and patients will likely develop functional disabilities. Although the adult brain can self-repair, the underlying mechanisms need further clarification.
Inflammation of the brain contributes to the effects of ischemic stroke. “There is evidence that more lipids are produced after tissue injuries and contribute to regulating inflammation,” says Takashi Shichita, senior author of the study. “We investigated the changes in lipid metabolite production in mice after ischemic stroke. Interestingly, the levels of a specific fatty acid called dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (DGLA) and its derivatives increased after the stroke.”
The researchers further discovered that a protein known as PLA2GE2 (Phospholipase A2 Group IIE, an enzyme) mediates DGLA increase. By manipulating the expression of PLA2GE2, they also showed its impact on functional recovery. Deficiency of PLA2GE2 led to more inflammation, lower expression of factors stimulating neuronal repair, and more tissue loss. The team carried on with identifying the targets of PLA2GE2/DGLA.
“When we look at genes expressed in mice lacking PLA2GE2, we found low levels of a protein called peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PADI4),” explains Akari Nakamura, lead author of the study. “PADI4 regulates transcription and inflammation. Remarkably, expressing PADI4 in mice limited the extent of tissue damage and inflammation after ischemic stroke!” Additionally, the study shows that PADI4 promotes the transcription of genes involved in brain repair. It also identifies the whole signaling pathway involved in this process.
Most data were obtained in a mouse model of ischemic stroke. Yet, the recovery pathway likely exists in humans as the researchers found that neurons surrounding the stroke site express PLA2G2E and PADI4 in humans. Moreover, another recent study reported that the lower serum DGLA level was correlated with the severe ischemic stroke and cognitive disorders in humans.
This study describes a new mechanism that triggers brain repair after an ischemic stroke, which might lead to the development of compounds promoting PADI4’s effects, that stimulate the recovery of patients. It could also change our current understanding and approach toward Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) or Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), as the only beneficial lipids for preventing atherosclerosis and vascular diseases. https://www.tmd.ac.jp/english/press-release/20230725-1/







Recent Comments