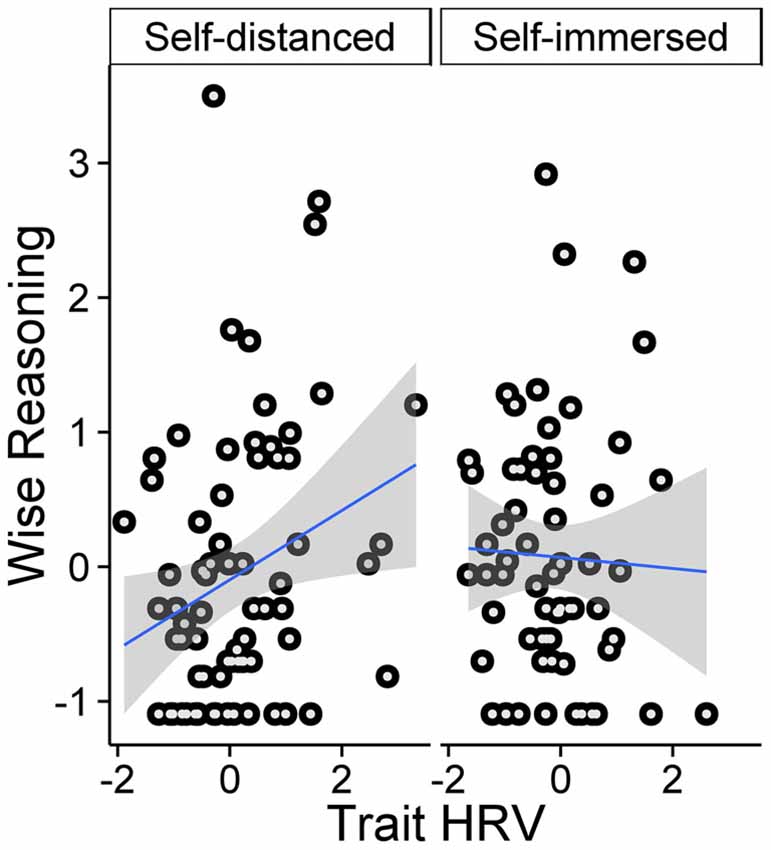
Self-distancing moderates the relationship between heart rate variability (HRV) and wise reasoning (z-scores). Scatterplot with line of best fit and 95% CI.
The study suggests heart rate variation and thinking process work together to enable wise reasoning about complex social issues. The work by Igor Grossmann, professor of psychology at Uni of Waterloo, and colleagues based at Australian Catholic University breaks new ground in wisdom research by identifying conditions under which psychophysiology impacts wise judgment.
A growing consensus among philosophers and cognitive scientists defines wise judgment to include the ability to recognize the limits of one’s knowledge, to be aware of the varied contexts of life and how they may unfold over time, to acknowledge others’ points of view, and to seek reconciliation of opposing viewpoints. The new study is the first to show that the physiology of the heart, specifically the variability of heart rate during low physical activity, is related to less biased, wiser judgment.
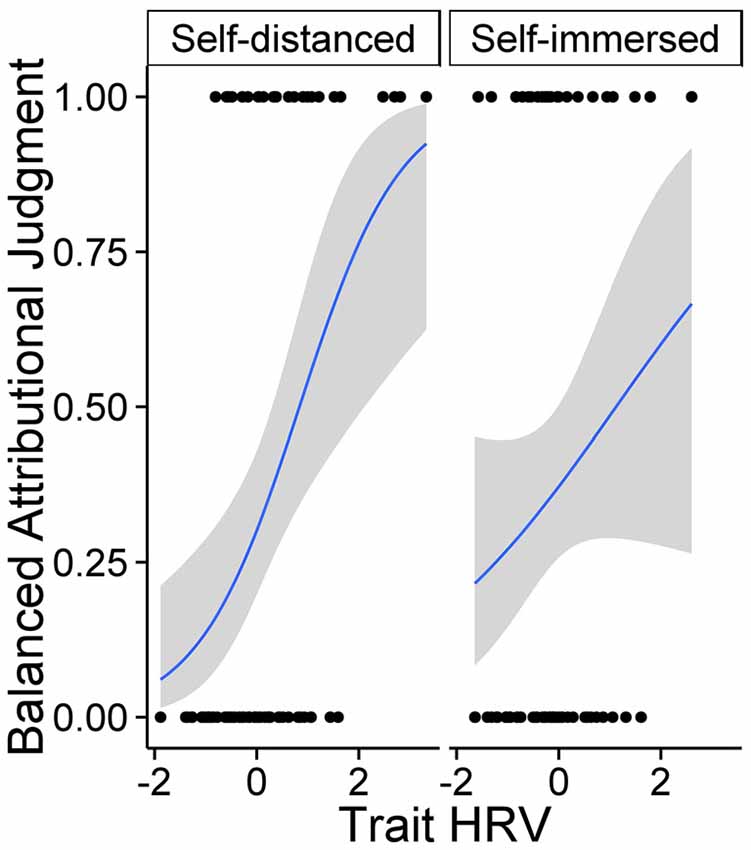
Self-distancing moderates the relationship between HRV (z-score) and balanced attributional judgment (dichotomous index). Log-likelihood estimates and 95% CI.
Human heart rate tends to fluctuate, even during steady-state conditions, such as while a person is sitting. Heart rate variability refers to the variation in the time interval between heartbeats and is related to the nervous system’s control of organ functions.
They found people with more varied heart rates were able to reason in a wiser, less biased fashion about societal problems when they were instructed to reflect on a social issue from a third-person perspective. But, when the study’s participants were instructed to reason about the issue from a first-person perspective, no relationship between heart rate and wiser judgment emerged.
“We already knew that people with greater variation in their heart rate show superior performance in the brain’s executive functioning such as working memory,” says Prof. Grossmann. “However, that does not necessarily mean these people are wiser – in fact, some people may use their cognitive skills to make unwise decisions. To channel their cognitive abilities for wiser judgment, people with greater heart rate variability first need to overcome their egocentric viewpoints.” The study opens the door for further exploration of wise judgment at the intersection of physiological and cognitive research. https://uwaterloo.ca/news/news/research-finds-wisdom-matter-both-heart-and-mind?utm_source=eurekalert&utm_medium=pressrelease&utm_campaign=Grossmann_Heart http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00068/full







Recent Comments