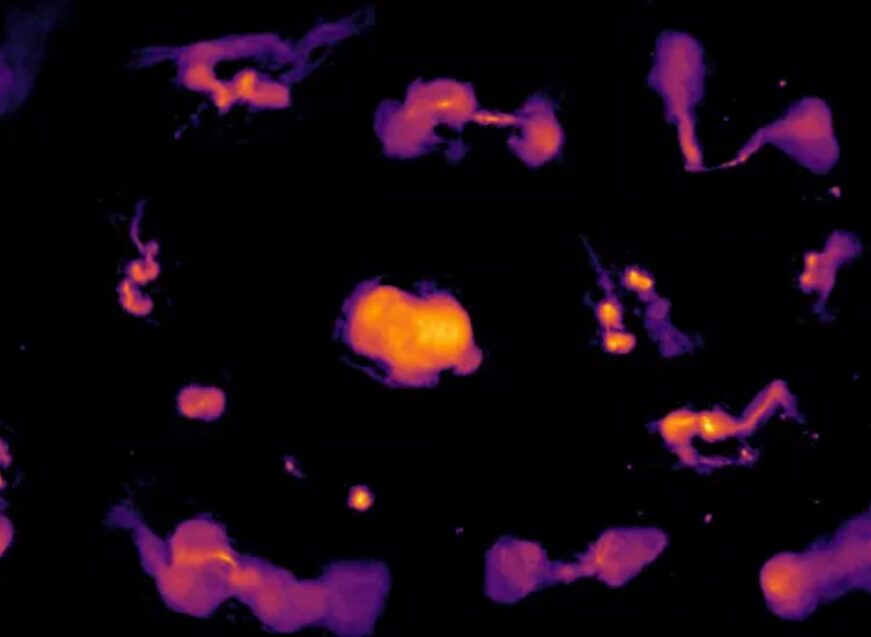
An international collaboration using the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) has published an exceptionally detailed radio sky map, revealing 13.7 million cosmic sources and delivering the most complete census yet of actively growing supermassive black holes. It showcases an extraordinary variety of systems powered by these black holes, whose radio emission can extend for millions of light-years.
The newly released LOFAR Two-meter Sky Survey (LoTSS-DR3) marks a major milestone in radio astronomy and international scientific collaboration. The results will be published in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
By observing the sky at low radio frequencies, the survey reveals a dramatically different view of the universe than that seen at optical wavelengths...
Read More






Recent Comments