
Due to our ever-increasing reliance on electronics, researchers are always on the lookout for battery materials with more desirable qualities. Common battery materials, like lithium, can be prone to disadvantages like overheating and material sourcing issues, leading to safety risks and higher costs.
Now, researchers from China have revealed a new battery design that may offer a better alternative to lithium...
Read More



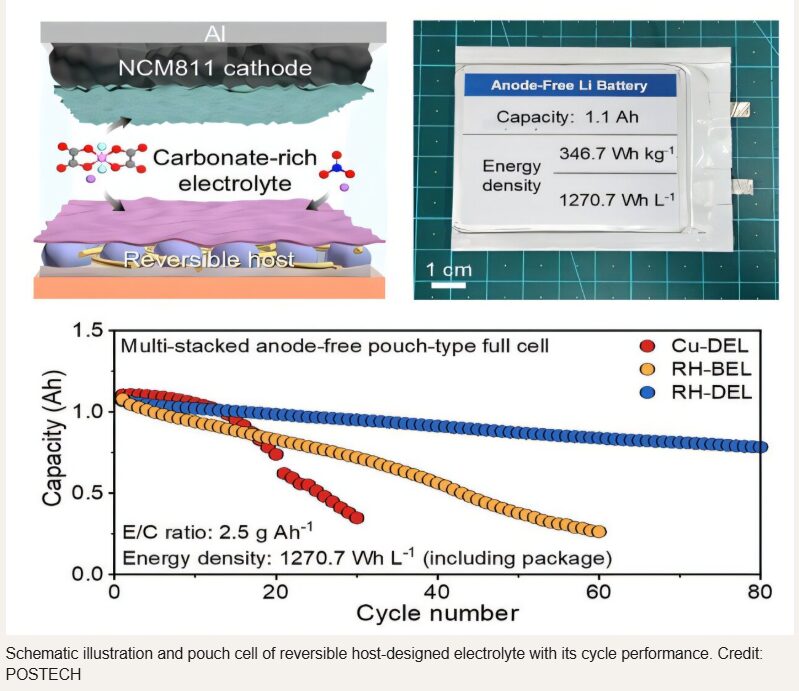
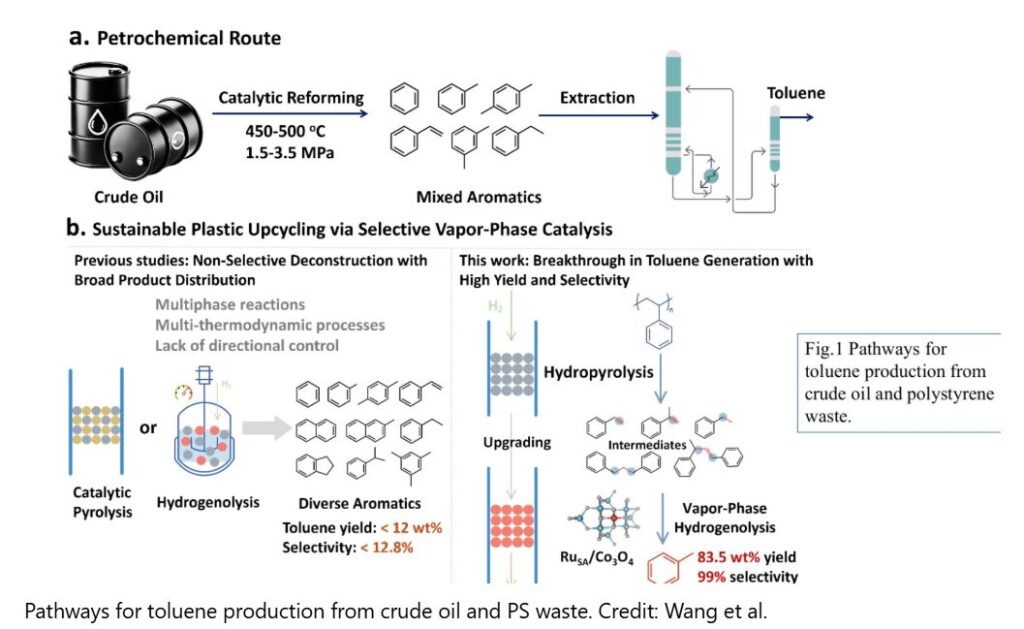


Recent Comments