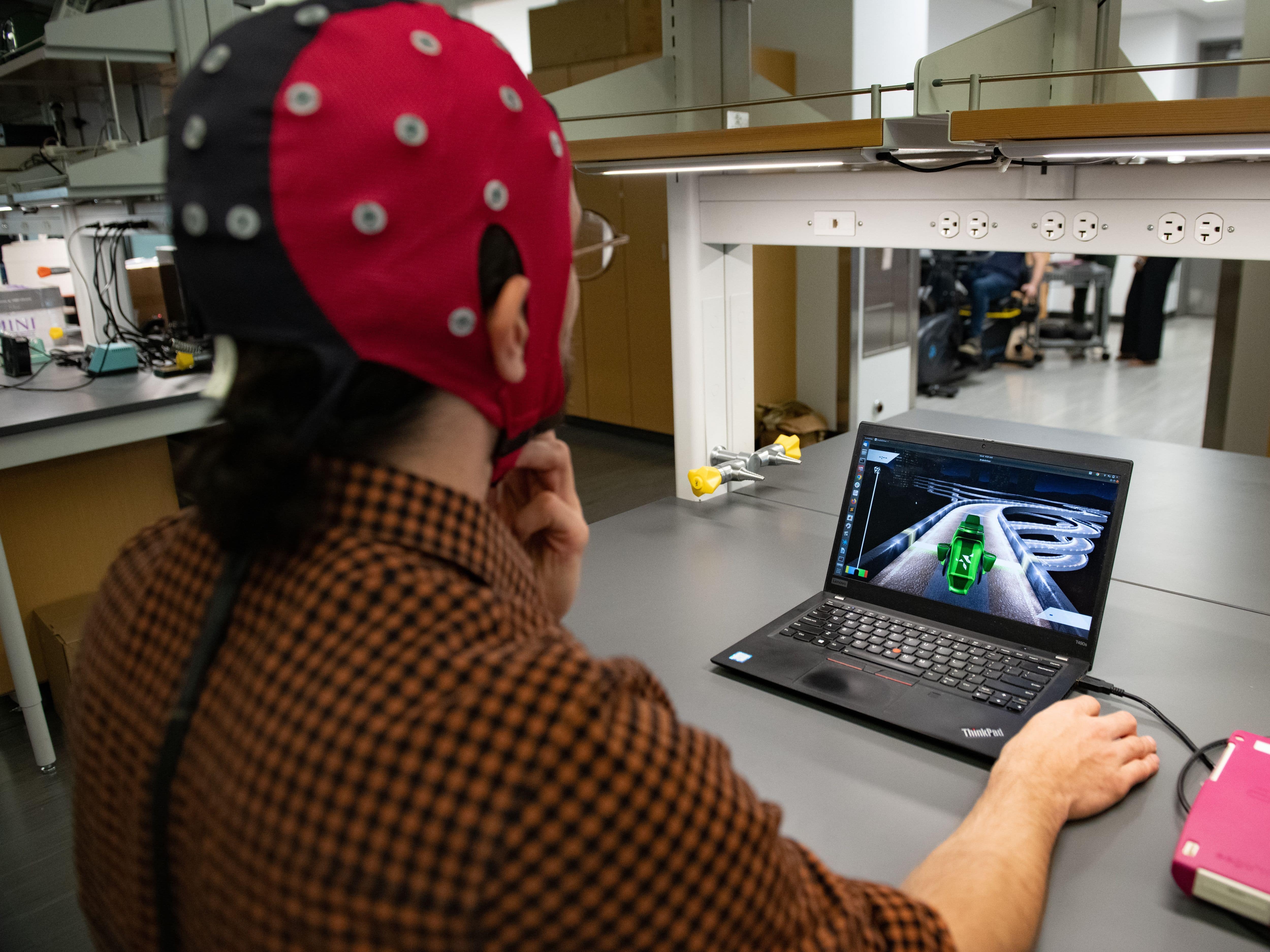

Engineers have created a brain-computer interface that doesn’t require calibration for each user, paving the way for widespread clinical applicability.
Imagine playing a racing game like Mario Kart, using only your brain to execute the complex series of turns in a lap.
This is not a video game fantasy, but a real program that engineers at The University of Texas at Austin have created as part of research into brain-computer interfaces to help improve the lives of people with motor disabiliti...
Read More








Recent Comments