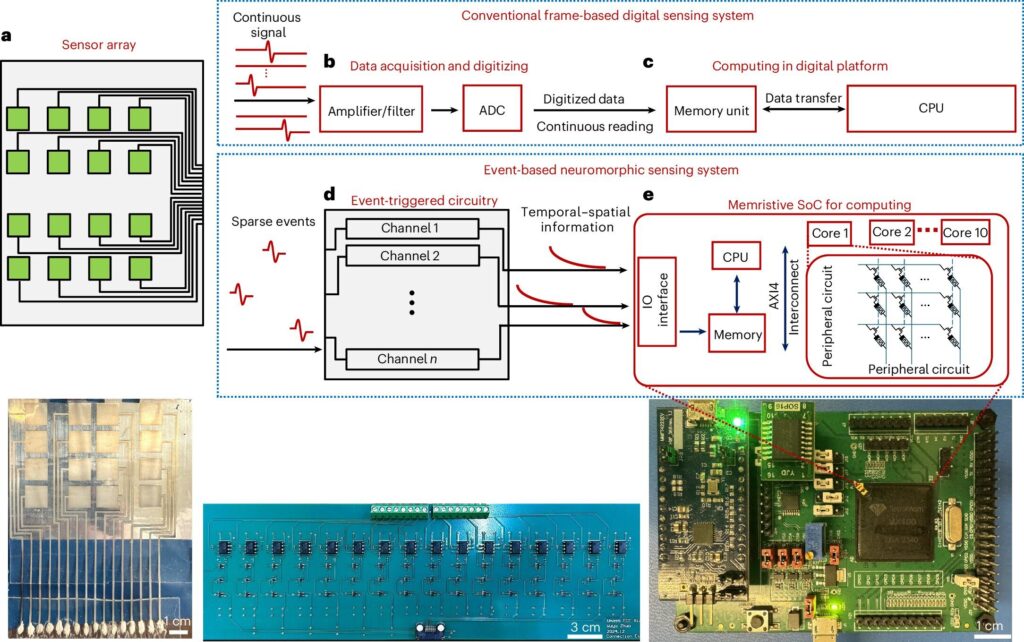
The ubiquity of smart devices—not just phones and watches, but lights, refrigerators, doorbells and more, all constantly recording and transmitting data—is creating massive volumes of digital information that drain energy and slow data transmission speeds. With the rising use of artificial intelligence in industries ranging from health care and finance to transportation and manufacturing, addressing the issue is becoming more pressing.
A research team led by the University of Massachusetts Amherst aims to address the problem wi...
Read More







Recent Comments