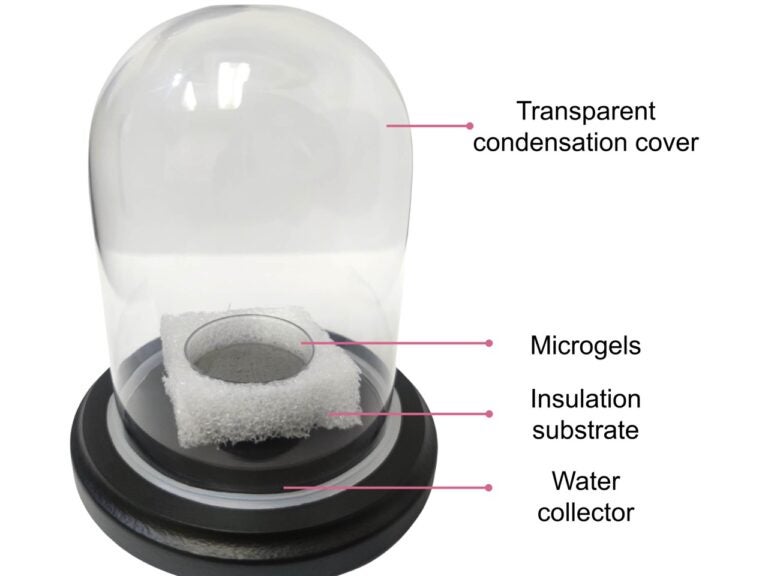

Researchers have focused on the moisture present in the air as a potential source of drinking water for drought-stressed populations. They reached a significant breakthrough in their efforts to create drinkable water out of thin air: a molecularly engineered hydrogel that can create clean water using just the energy from sunlight.
For significant portions of the globe faced with water shortage problems, a beacon of hope may be on the way: the ability to easily turn hot air into drinking water.
For the past few years, researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have focused on the moisture present in the air as a potential source of drinking water for drought-stressed populations...
Read More







Recent Comments