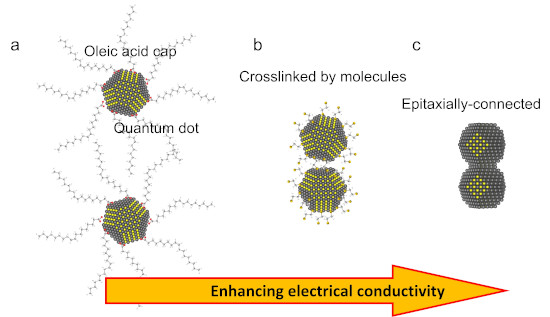
Researchers from the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science and collaborators have succeeded in creating a “superlattice” of semiconductor quantum dots that can behave like a metal, potentially imparting exciting new properties to this popular class of materials.
Semiconducting colloidal quantum dots have garnered tremendous research interest due to their special optical properties, which arise from the quantum confinement effect...
Read More








Recent Comments