Category Physics


Minimally invasive surgery and automated robot-guided surgery are likely to be performed under extreme conditions, which require new demands on intraoperative information acquisition capabilities. Three-dimensional (3D) brain point cloud generation plays an essential role in overcoming the visual limitations of these surgeries.
One of the applications of generative AI is in the field of 3D brain point cloud generation. By using deeplearning algorithms, the 3D point cloud of the patient’s brain can be generated for reconstruction during minimally invasive surgery. However, some conventional existing point cloud reconstruction methods still have limitations when applied directly to real surgical scenarios.
Now, a research team led by Prof...
Read More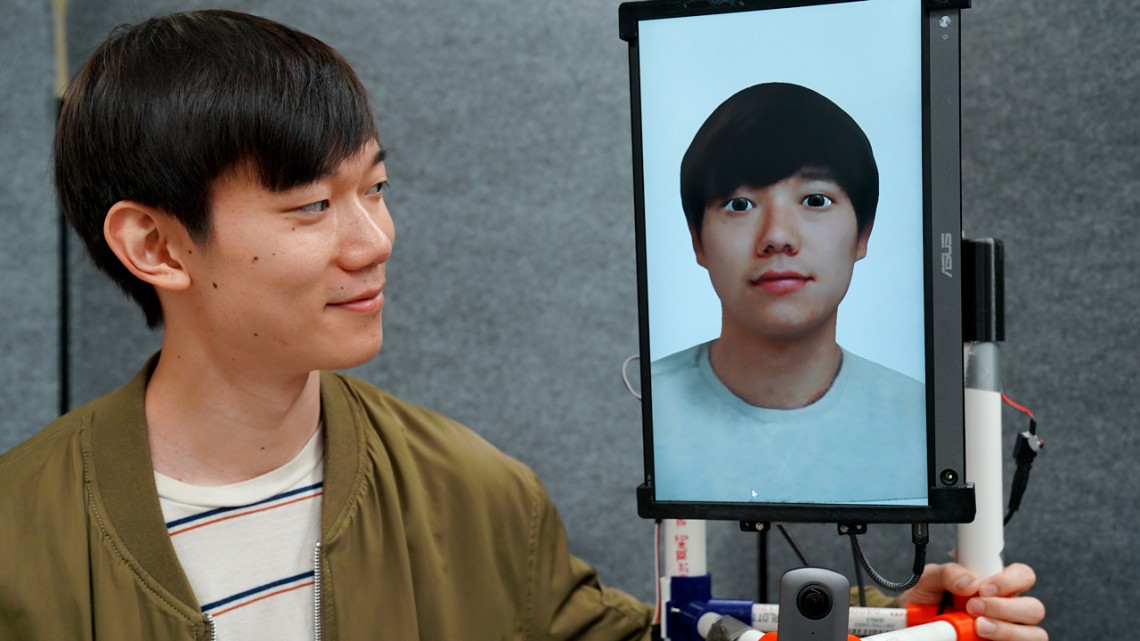
Cornell University researchers have developed a robot, called ReMotion, that occupies physical space on a remote user’s behalf, automatically mirroring the user’s movements in real time and conveying key body language that is lost in standard virtual environments.
“Pointing gestures, the perception of another’s gaze, intuitively knowing where someone’s attention is — in remote settings, we lose these nonverbal, implicit cues that are very important for carrying out design activities,” said Mose Sakashita, a doctoral student of information science.
Sakashita is the lead author of “ReMotion: Supporting Remote Collaboration in Open Space with Automatic Robotic Embodiment,” which he prese...
Read More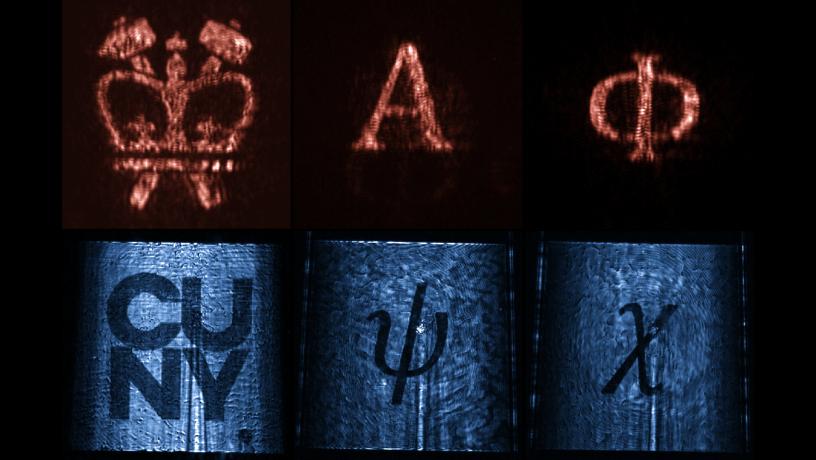
Researchers at Columbia Engineering have developed a new class of integrated photonic devices – “leaky-wave metasurfaces” – that can convert light initially confined in an optical waveguide to an arbitrary optical pattern in free space...
Read More






Recent Comments