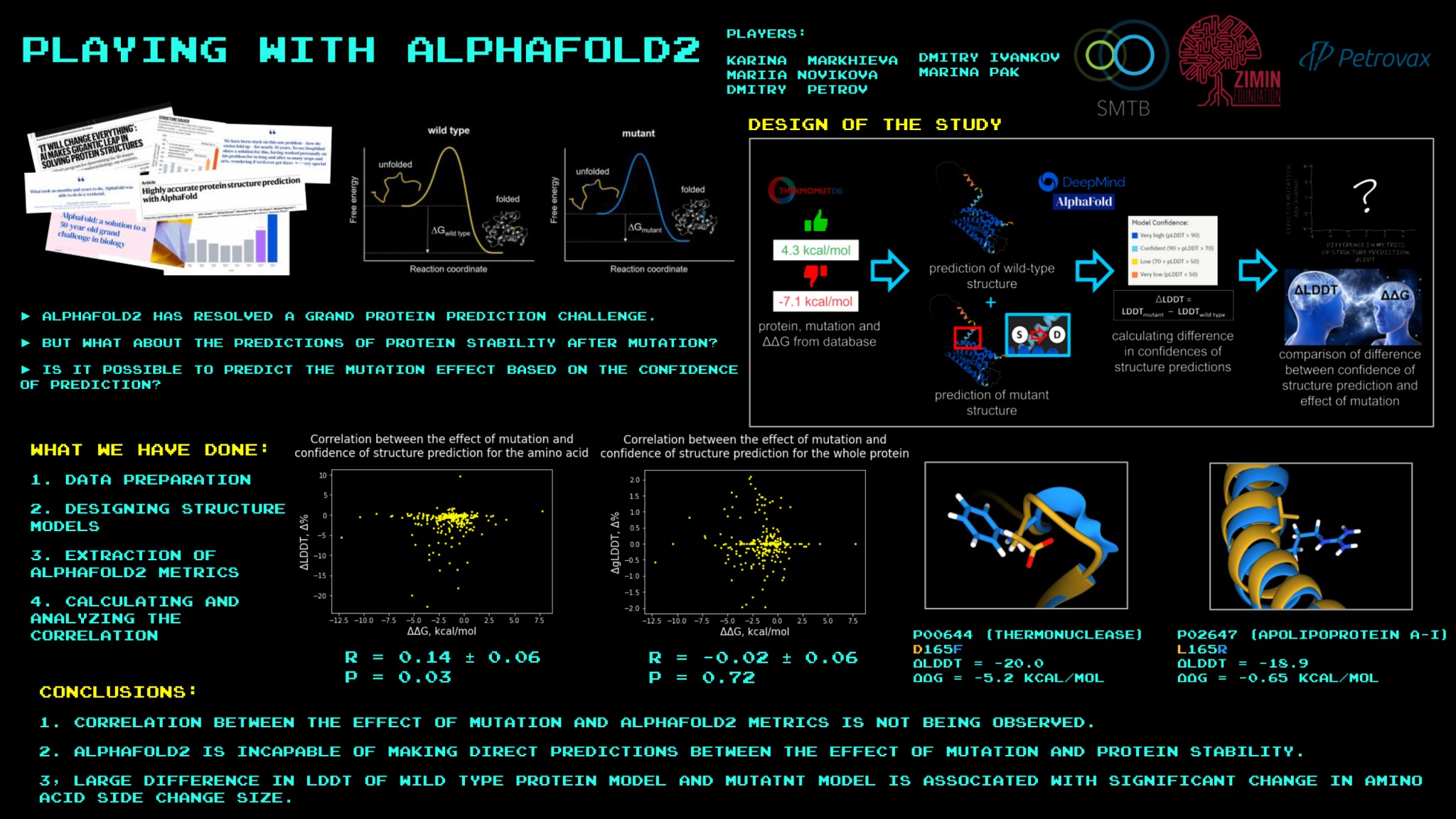
A bioinformatics boot camp for high schoolers at Skoltech turned into a venue for the latest chapter in the ongoing contest between humans and artificial intelligence in science. Having earlier resolved a key 50-year-old problem of structural bioinformatics, the breakthrough AI program AlphaFold proved inapplicable to another challenge researchers in this field are faced with.
This finding is reported in a PLOS ONE study, whose authors refute the claims by some AlphaFold enthusiasts that DeepMind’s AI has mastered the ultimate protein physics and is the be-all and end-all of structural bioinformatics.
Structural bioinfor...
Read More







Recent Comments