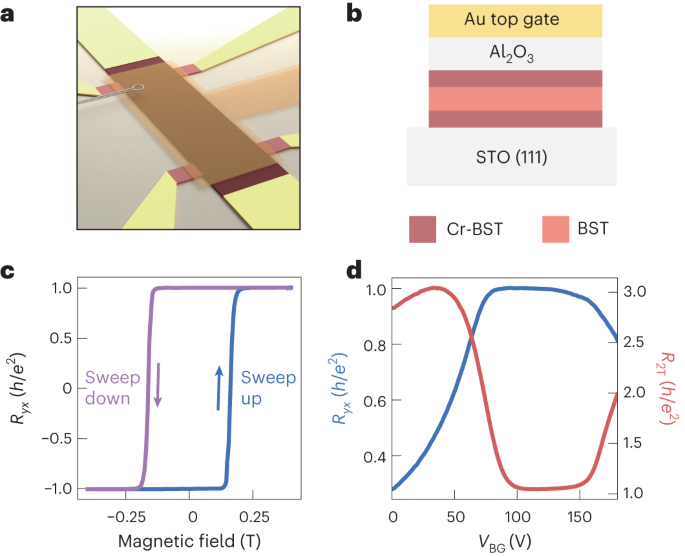
Cornell has used magnetic imaging to obtain the first direct visualization of how electrons flow in a special type of insulator, and by doing so they discovered that the transport current moves through the interior of the material, rather than at the edges, as scientists had long assumed.
The finding provides new insights into the electron behavior in so-called quantum anomalous Hall insulators and should help settle a decades-long debate about how current flows in more general quantum Hall insulators. These insights will inform the development of topological materials for next-generation quantum devices.
The team’s paper, “Direct Visualization of Electronic Transport in a Quantum Anomalous Hall Insulator,” published Aug...
Read More








Recent Comments