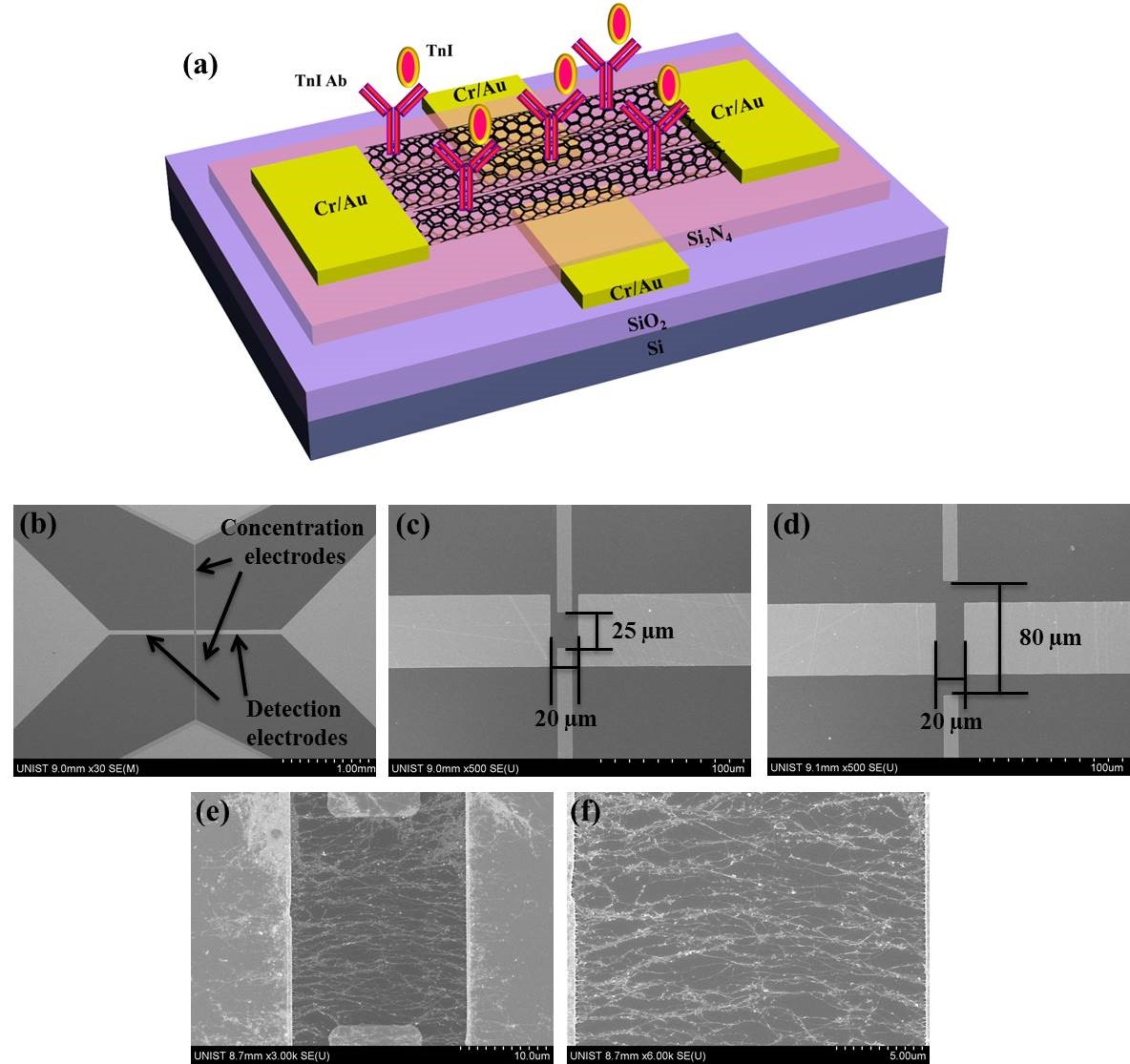
A schematic diagram of the SWCNT electrical immunosensor with two pairs of concentration and detection electrodes.
An electrical immunosensor has been developed to detect acute myocardial infarction within a minute. The system works by measuring the level of cardiac troponin I (cTnI), a protein that is excreted by the heart muscle into the blood following a heart attack. Prof. Jang states, “This new immunosensor is constructed in a different way than any other sensor.” He adds, “Owing to the new design of this immunosensor, this device is able to rapidly diagnose the level of heart attacks at the point of care.”
It is a a rapid, label-free, and highly sensitive single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) electrical immunosensor, featuring two pairs of electrodes. These immunosensors showed high specificity over another cardiac biomarker, myoglobin, TBE medium (0.0025×), and 500-fold diluted human serum. According to the research team, this novel immunosensor holds considerable potential for use as a platform for sensing distinct types of proteins, along with the feasibility of miniaturization and integration for biomedical diagnosis.
http://news.unist.ac.kr/new-study-seeks-to-use-human-serum-to-detect-heart-attacks/ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956566316302470






Recent Comments