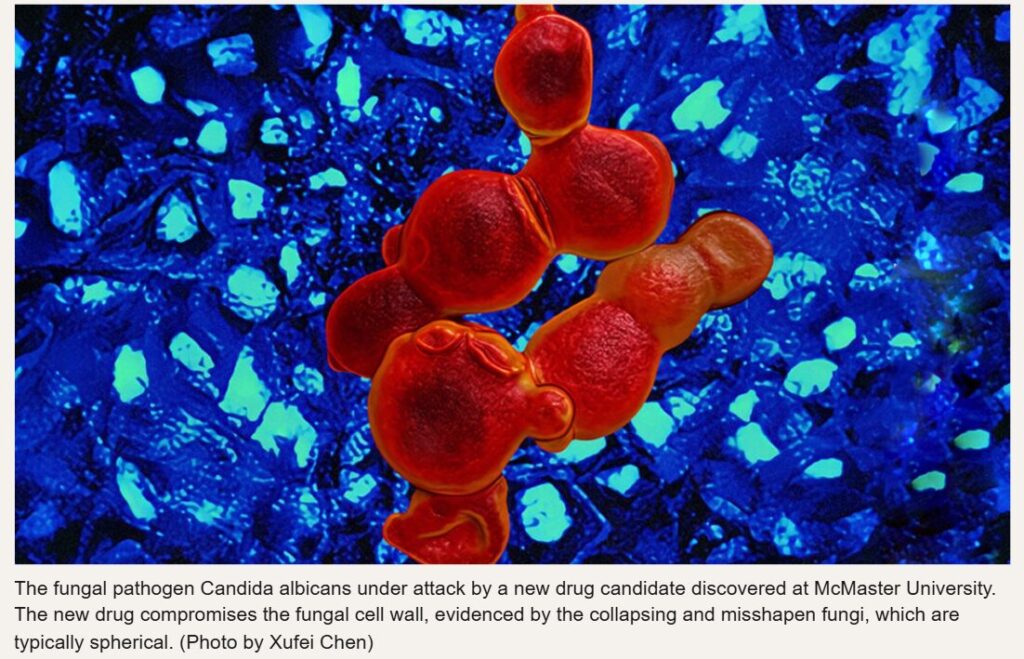
Fungal infections kill millions of people each year, and modern medicine is struggling to keep up. But researchers at McMaster University have identified a molecule that may help turn the tide—butyrolactolA, a chemical compound that targets a deadly, disease-causing fungi called Cryptococcus neoformans.
Infections caused by Cryptococcus are extremely dangerous. The pathogen, which can cause pneumonia-like symptoms, is notoriously drug-resistant, and it often preys on people with weakened immune systems, like cancer patients or those living with HIV. And the same can be said about other fungal pathogens, like Candida auris or Aspergillus fumigatus—both of which, like Cryptococcus, have been declared priority pathogens by the World Health Organization.
Despite the threat, thou...
Read More













Recent Comments