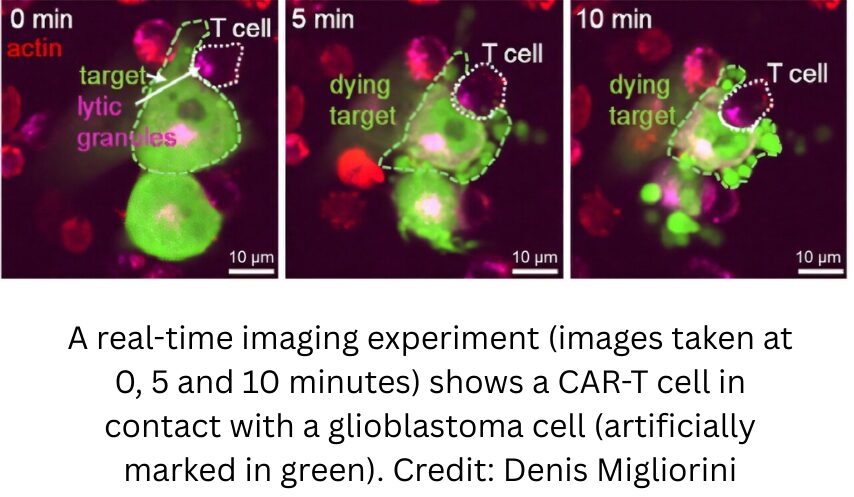
With a five-year survival rate of less than 5%, glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive types of brain cancer. Until now, all available treatments, including immunotherapy—which involves strengthening the immune system to fight cancer—have proved disappointing. CAR-T cells are genetically modified immune cells manufactured in the laboratory and designed to identify and destroy cancer cells.
By targeting a protein present in the tumor environment, a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the Geneva University Hospital (HUG) has developed CAR-T cells capable of destroying glioblastoma cells. Their efficacy in an animal model of the disease paves the way for clinical trials in humans.
The results are published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.
Glioblasto...
Read More












Recent Comments