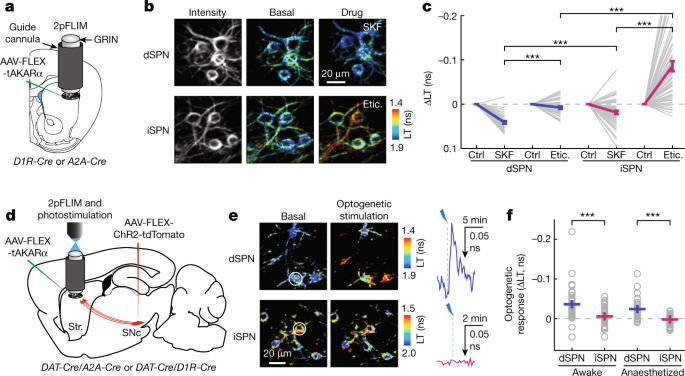
Discovery could immediately suggest new avenues for drug development. Researchers at Oregon Health & Science University have discovered that the neurotransmitter adenosine effectively acts as a brake to dopamine, another well-known neurotransmitter involved in motor control.
Scientists found that adenosine operates in a kind of push-pull dynamic with dopamine in the brain; the discovery published today in the journal Nature.
“There are two neuronal circuits: one that helps promote action and the other that inhibits action,” said senior author Haining Zhong, Ph.D., scientist with the OHSU Vollum Institute...
Read More




Recent Comments