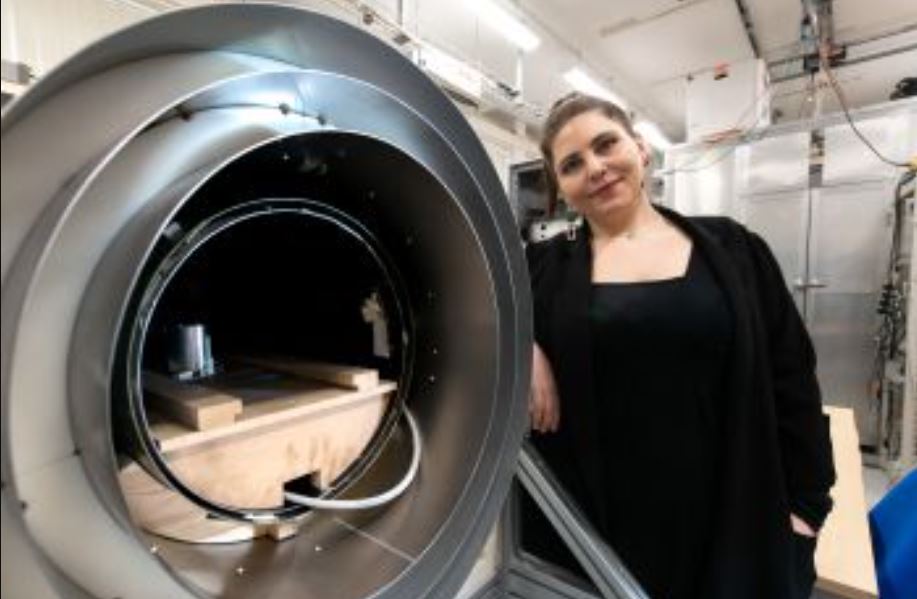

New highly sensitive quantum sensors for the brain may in the future be able to identify brain diseases such as dementia, ALS and Parkinson’s, by spotting a slowing in the speed at which signals travel across the brain. The research findings from a paper led by University of Sussex quantum physicists are published in Scientific Reports journal.
The quantum scanners being developed by the scientists can detect the magnetic fields generated when neurons fire. Measuring moment-to-moment changes in the brain, they track the speed at which signals move across the brain...
Read More





Recent Comments