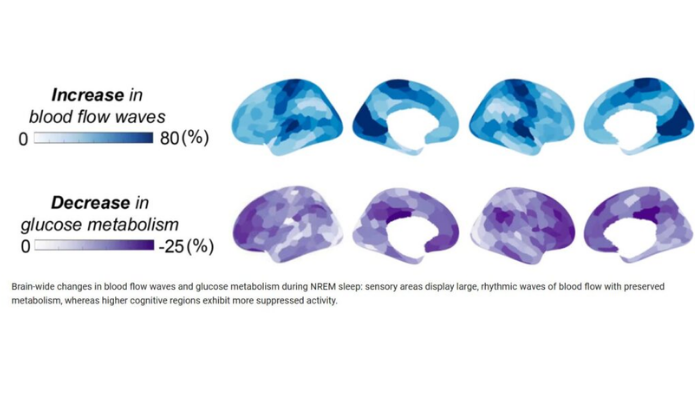
A new study by investigators from Mass General Brigham has used next-generation imaging technology to discover that when the brain is falling asleep, it shows a coordinated shift in activity.
The researchers found that during NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep, parts of the brain that handle movement and sensory input stay active and keep using energy, while areas involved in thinking, memory and daydreaming quiet down and use less energy. Their results are published in Nature Communications.
“This research helps explain how the brain stays responsive to the outside world even as awareness fades during sleep,” said corresponding author Jingyuan Chen, Ph.D., an assistant investigator at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging at Massachusetts General Hospital.
...Read More





Recent Comments