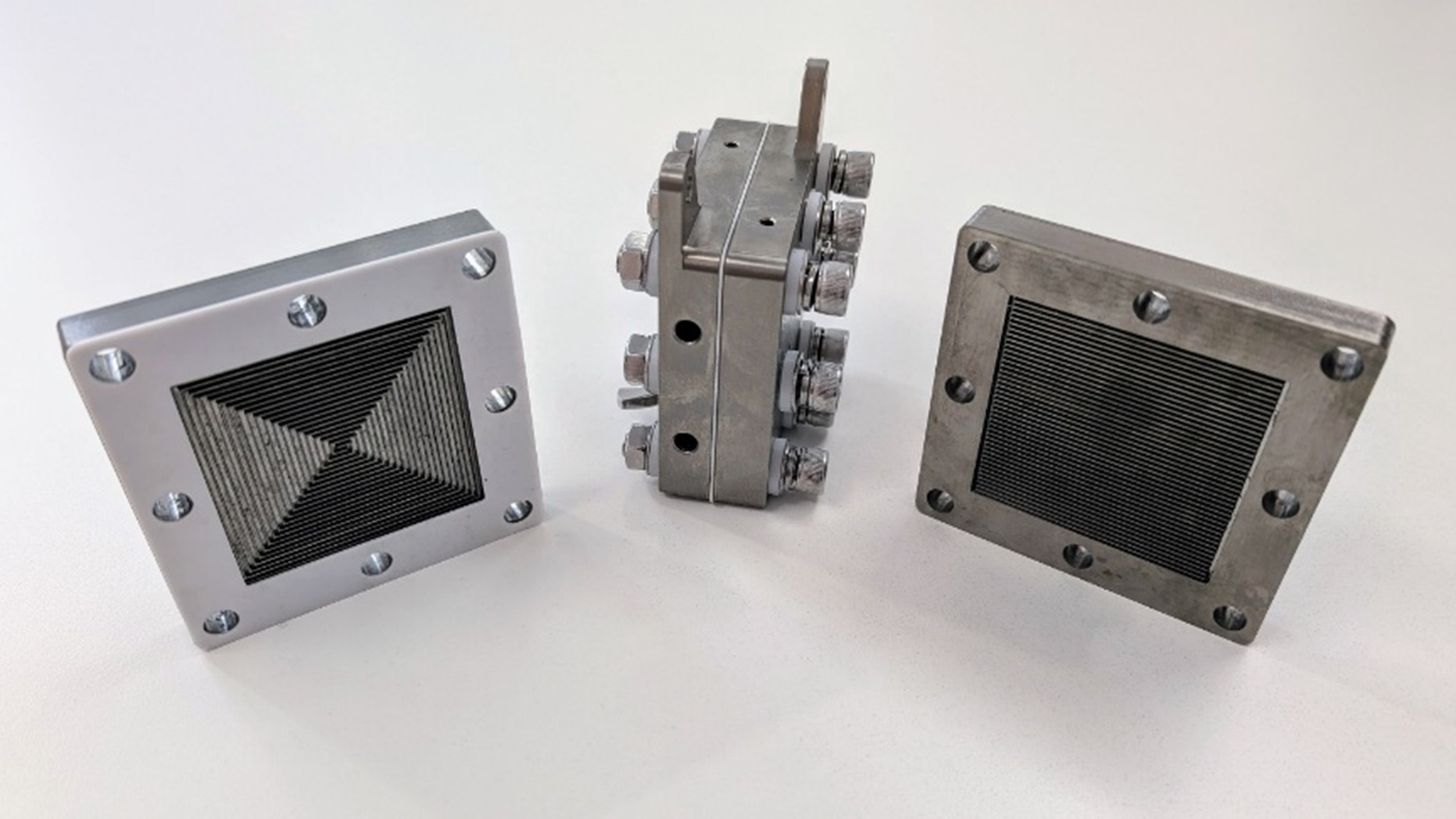
University of Sydney researchers have harnessed human-made lightning to develop a more efficient method of generating ammonia—one of the world’s most important chemicals. Ammonia is also the main ingredient of fertilizers that account for almost half of all global food production.
The research was published in Angewandte Chemie International edition.
The team have successfully developed a more straightforward method to produce ammonia (NH3) in gas form. Previous efforts by other laboratories produced ammonia in a solution (ammonium, NH4+), which requires more energy and processes to transform it into the final gas product.
The current method to generate ammonia, the Hab...
Read More





Recent Comments