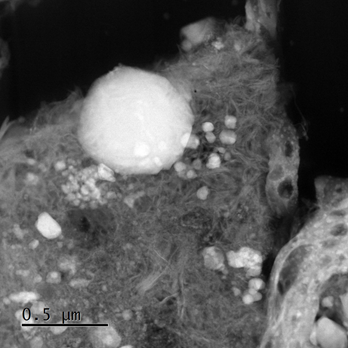
The UK’s national synchrotron facility, Diamond Light Source, was used by a large, international collaboration to study grains collected from a near-Earth asteroid to further our understanding of the evolution of our solar system.
Researchers from the University of Leicester brought a fragment of the Ryugu asteroid to Diamond’s Nanoprobe beamline I14 where a special technique called X-ray Absorption Near Edge Spectroscopy (XANES) was used to map out the chemical states of the elements within the asteroid material, to examine its composition in fine detail...
Read More




Recent Comments