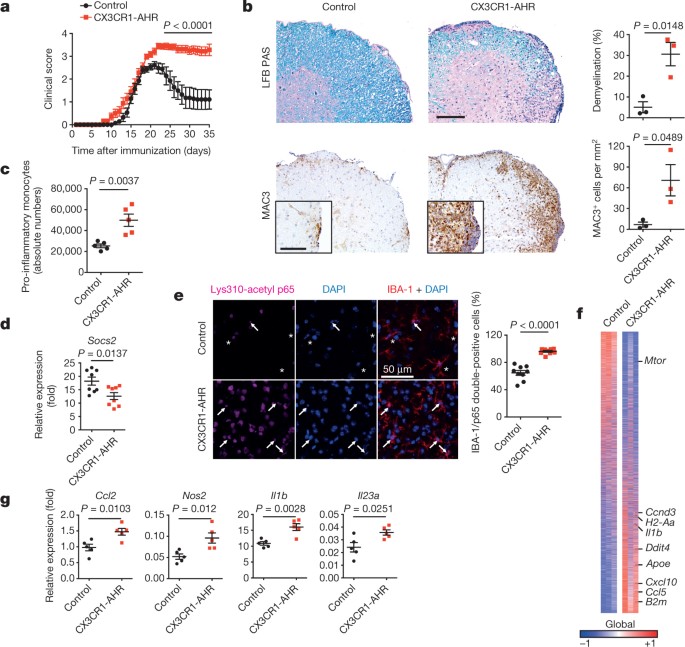
AHR limits microglial pro-inflammatory transcriptional responses during EAE.
A study published this week in Nature sheds new light on the connection between the gut and the brain, untangling the complex interplay that allows the byproducts of microorganisms living in the gut to influence the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) have been using both animal models and human cells from patients to tease out the key players involved in the gut-brain connection as well as in the crosstalk between immune cells and brain cells. Their new publication defines a pathway that may help guide therapies for multiple sclerosis and other neurologic diseases.
The new research focuses on the influence of gut microbes on two types of cells that play...
Read More




Recent Comments