Researchers have described a new antibiotic that appears to have the potential to cure Lyme disease. As if COVID and RSV weren’t bad enough, incidents of Lyme disease — a potentially serious disease caused by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi and transmitted following a bite of an infected deer tick — also are on the rise in the United States.
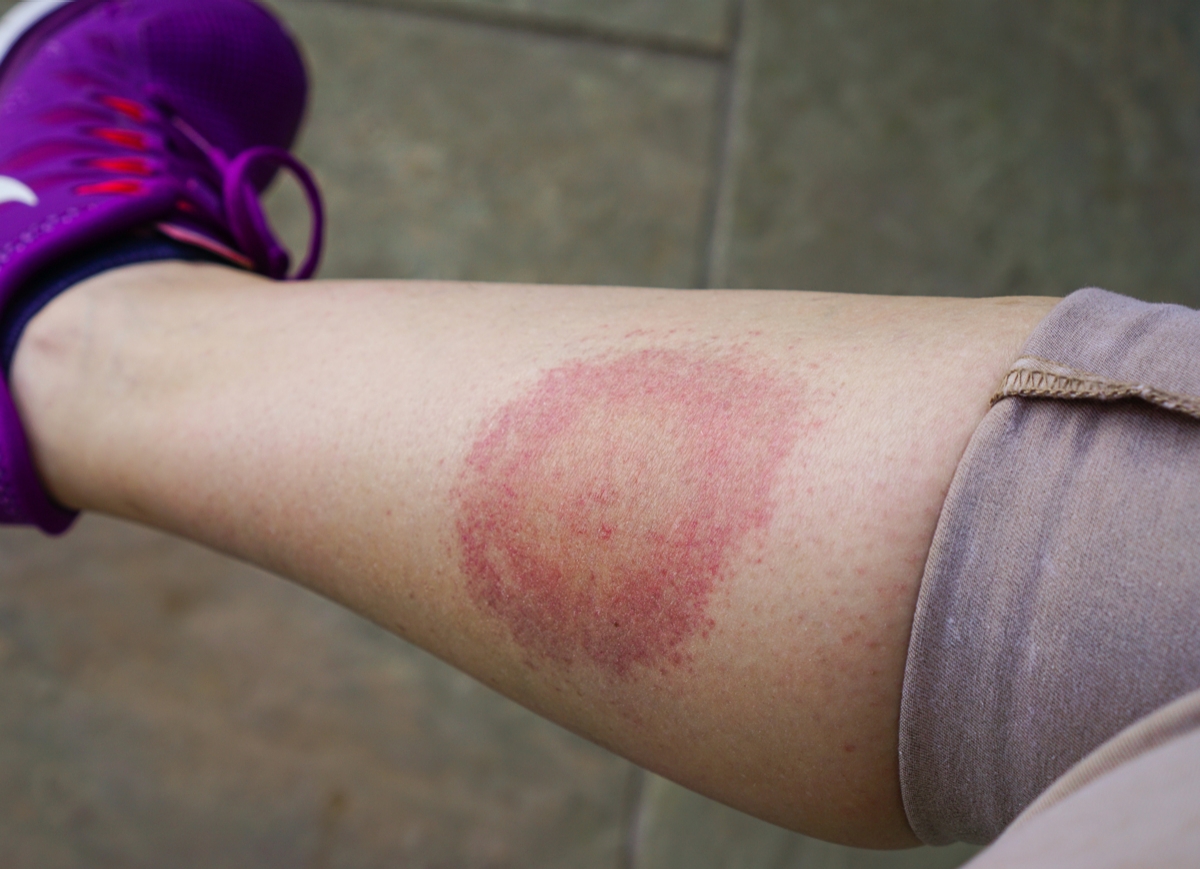
Lyme disease affects an estimated 300,000 people in the United States alone. Humans and animals can be infected with B. burgdorferi following the bite of an infected deer tick, also known as the black-legged tick. About 80% of those who contract the disease will develop a bulls-eye rash (erythema migrans) around or near the site of the bite anywhere from three to 30 days following the bite.
Although early antibiotic treatment is effective ...
Read More







Recent Comments