
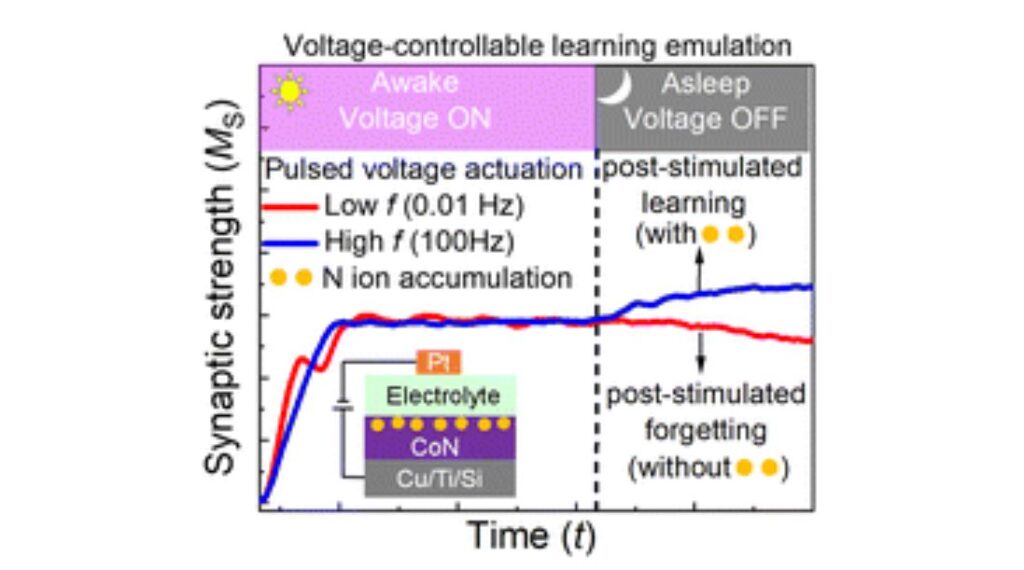
Theoretical physicists at Utrecht University, together with experimental physicists at Sogang University in South Korea, have succeeded in building an artificial synapse. This synapse works with water and salt and provides the first evidence that a system using the same medium as our brains can process complex information.
The results appear in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In the pursuit of enhancing the energy efficiency of conventional computers, scientists have long turned to the human brain for inspiration. They aim to emulate its extraordinary capacity in various ways.
These efforts hav...
Read More




Recent Comments