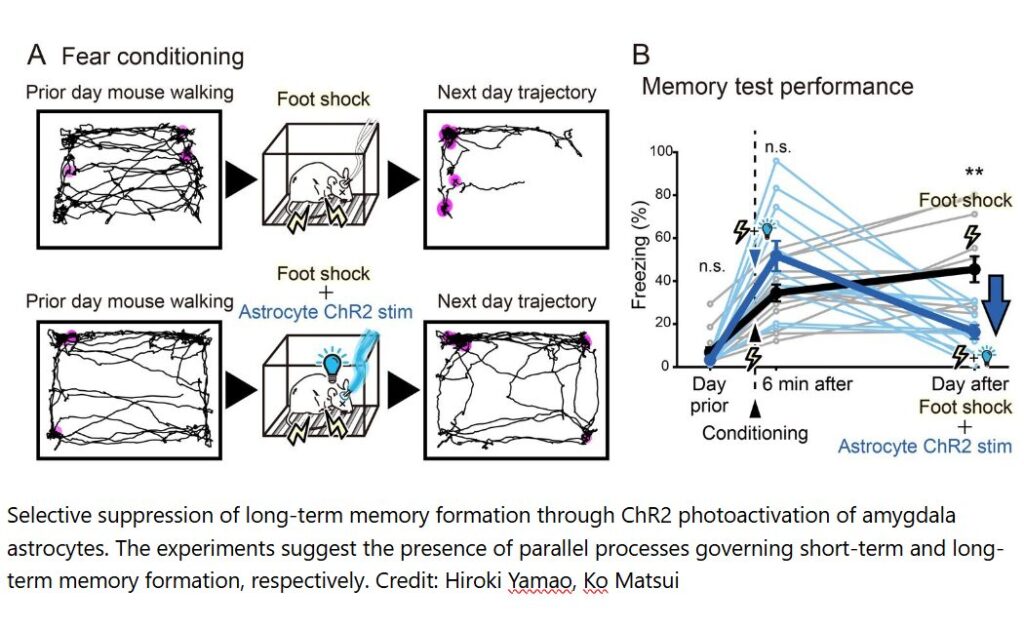
One of the most powerful assets of the brain is that it can store information as memories, allowing us to learn from our mistakes. However, some memories remain vivid while others become forgotten. Unlike computers, our brains appear to filter which memories are salient enough to store.
Researchers from Tohoku University have discovered that part of the memory selection process depends on the function of astrocytes, a special type of cell that surrounds neurons in the brain. They showed that artificially acidifying the astrocytes did not affect short-term memory but prevented memories from being remembered long-term.
The findings are published in the journal Glia.
The researchers implemented a technique called “optogenetics” to manipulate the astrocytes by shining light onto ...
Read More







Recent Comments