
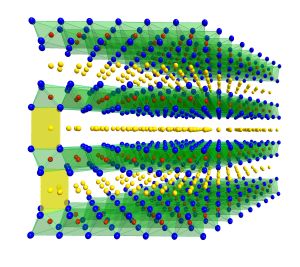
Drexel University researchers have developed two new electrode designs, using MXene material, that will allow batteries to charge much faster. The key is a microporous design that allows ions to quickly make their way to redox active sites. Credit: Drexel University
Researchers use mxene to push charging rate limits in energy storage. Can you imagine fully charging your cell phone in just a few seconds? Researchers in Drexel University’s College of Engineering can, and they took a big step toward making it a reality with their recent work unveiling of a new battery electrode design...
Read More







Recent Comments