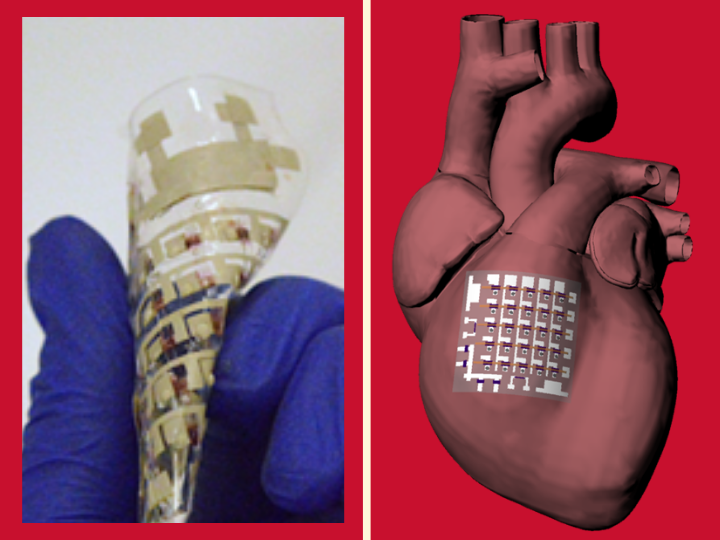
Researchers reported developing a cardiac patch made from fully rubbery electronics that can be placed directly on the heart to collect electrophysiological activity, temperature, heartbeat and other indicators, all at the same time.
Pacemakers and other implantable cardiac devices used to monitor and treat arrhythmias and other heart problems have generally had one of two drawbacks — they are made with rigid materials that can’t move to accommodate a beating heart,...
Read More





Recent Comments