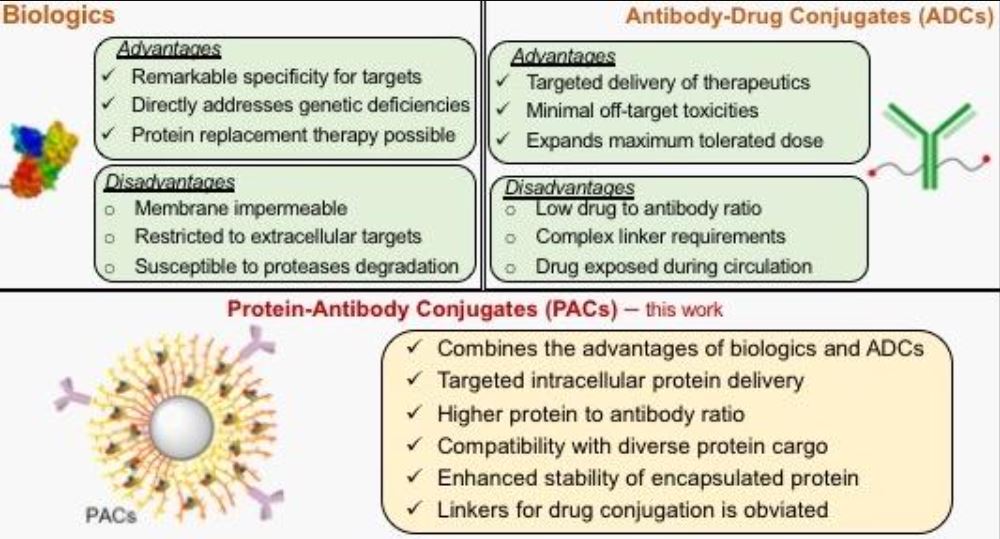
Latest advance in targeted delivery of therapeutic proteins. A team of researchers at the Center for Bioactive Delivery at the University of Massachusetts Amherst’s Institute for Applied Life Sciences has engineered a nanoparticle that has the potential to revolutionize disease treatment, including for cancer. This new research, which appears today in Angewandte Chemie, combines two different approaches to more precisely and effectively deliver treatment to the specific cells affected by cancer.
Two of the most promising new treatments involve delivery of cancer-fighting drugs via biologics or antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Each has its own advantages and limitations...
Read More






Recent Comments