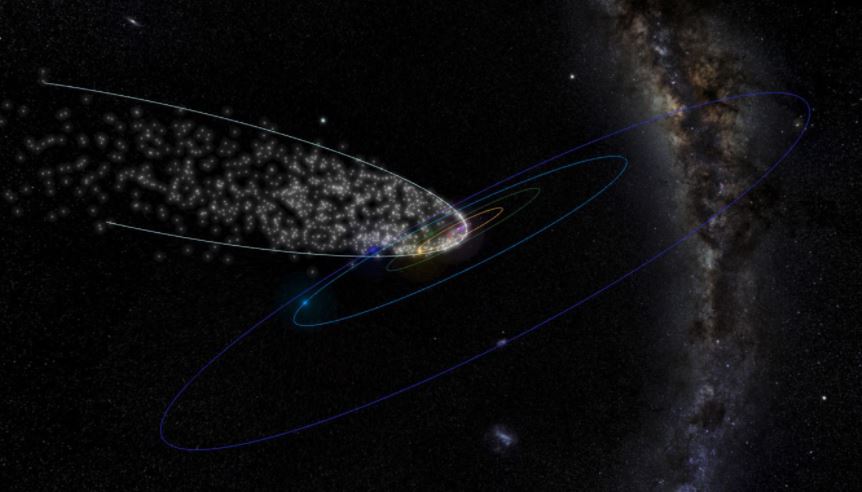
Researchers report that they can detect showers from the debris in the path of comets that pass close to Earth orbit and return as infrequently as once every 4,000 years.
Comets that circle the Sun in very elongated orbits spread their debris so thin along their orbit or eject it out of the solar system altogether that their meteor showers are hard to detect. From a new meteor shower survey published in the journal Icarus, researchers now report that they can detect showers from the debris in the path of comets that pass close to Earth orbit and are known to return as infrequent as once every 4,000 years.
“This creates a situational ...
Read More




Recent Comments