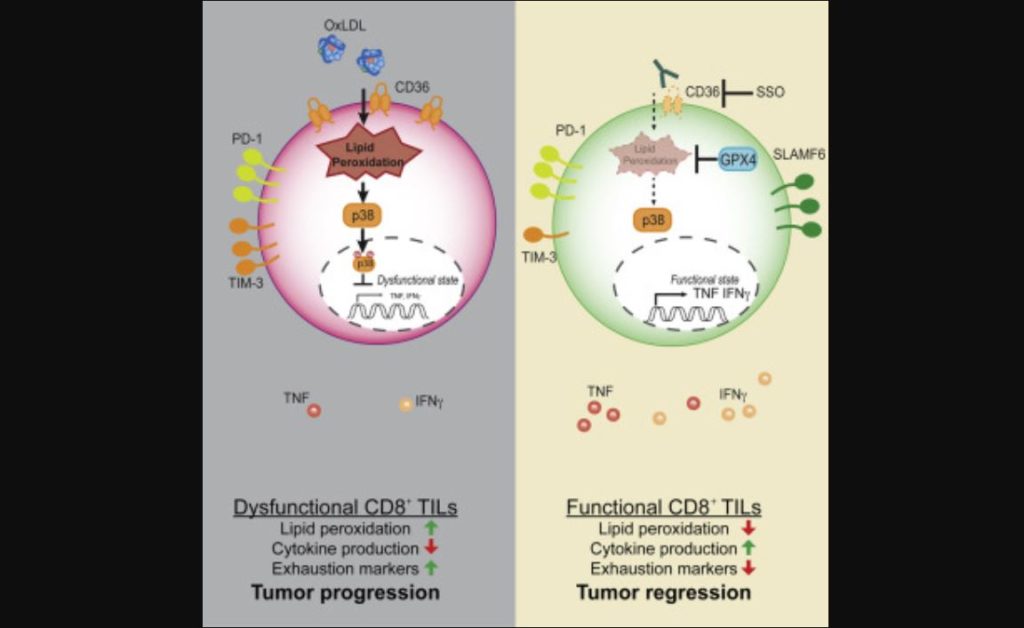
In order for cancer to grow and spread, it has to evade detection by our immune cells, particularly specialized “killer” T cells. Salk researchers led by Professor Susan Kaech have found that the environment inside tumors (the tumor microenvironment) contains an abundance of oxidized fat molecules, which, when ingested by the killer T cells, suppresses their ability to kill cancer cells. In a vicious cycle, those T cells, in need of energy, increase the level of a cellular fat transporter, CD36, that unfortunately saturates them with even more oxidized fat and further curtails their anti-tumor functions.
The discovery, published online in Immunity on June 7, 2021, suggests new pathways for safeguarding the immune system’s ability to fight cancer by reducing the oxidative lipid dama...
Read More





Recent Comments