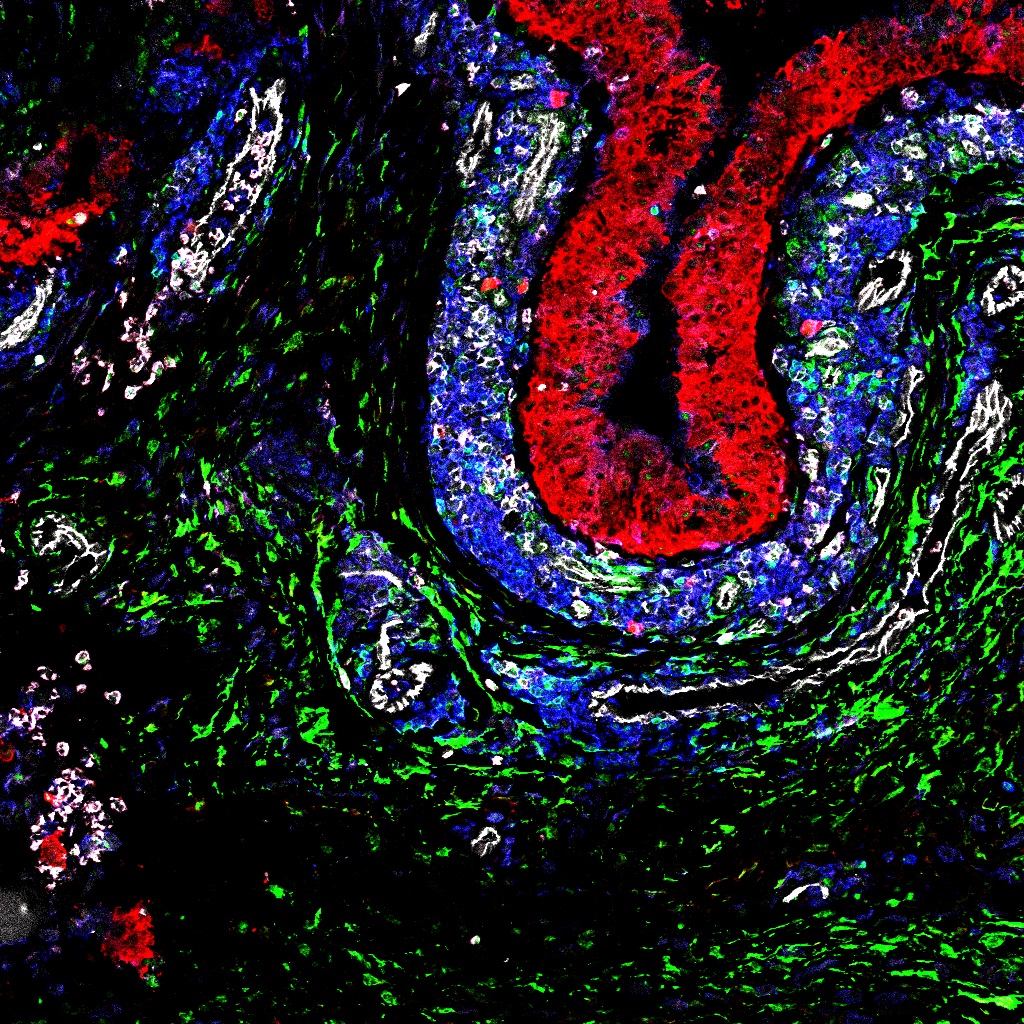
Synovial Fibroblasts (SFs) are cells that make up part of the connective tissue, or synovium, around human joints. In RA patients, SF cells cause damage by invading and attacking the cartilage and bone around the joint
A study reveals the key role of different types of fibroblast cells in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), opening up a new avenue for research into treatment of the disease. Synovial Fibroblasts (SFs) are cells that make up part of the connective tissue, or synovium, around human joints. In RA patients, SF cells cause damage by invading and attacking the cartilage and bone around the joint.
A team from University of Birmingham’s Institute of Inflammation and Ageing identified 2 distinct types of SF within the synovial membrane...
Read More




Recent Comments