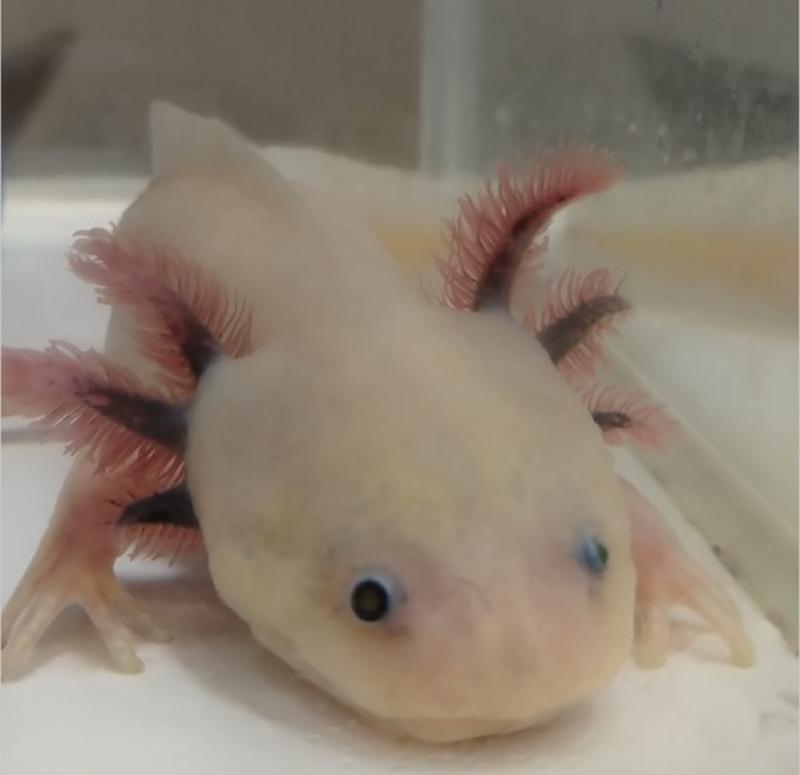

Keratinocytes produce collagen fibers, while deeper fibroblasts later modify the collagen fibers initially formed by keratinocytes. Challenging the long-standing belief that fibroblasts produce skin collagen, researchers at Okayama University have investigated collagen formation in the ‘glass-skinned’ amphibian axolotl and other vertebrates. They discovered that keratinocytes, the surface cells of the skin, are responsible for producing collagen, which is then transferred deeper to form the dermis. Later, fibroblasts migrate into this collagen layer, modifying and reinforcing its structure.
The skin consists of two primary layers...
Read More






Recent Comments