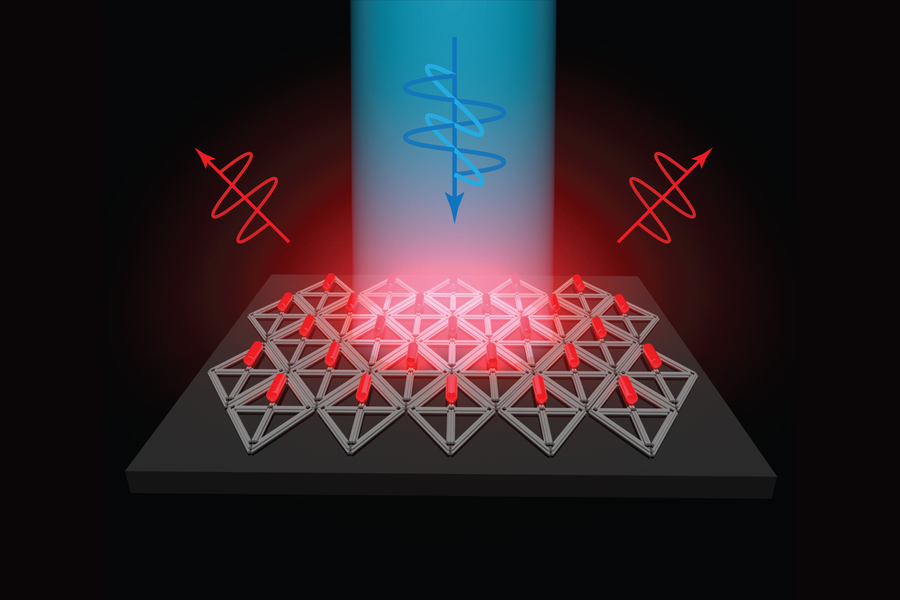
MIT engineers developed a new way to create these arrays, by scaffolding quantum rods onto patterned DNA. Using scaffolds of folded DNA, engineers assembled arrays of quantum rods with desirable photonic properties that could enable them to be used as highly efficient micro-LEDs for televisions or virtual reality devices.
Flat screen TVs that incorporate quantum dots are now commercially available, but it has been more difficult to create arrays of their elongated cousins, quantum rods, for commercial devices. Quantum rods can control both the polarization and color of light, to generate 3D images for virtual reality devices.
Using scaffolds made of folded DNA, MIT engineers have come up with a new way to precisely assemble arrays of quantum rods...
Read More






Recent Comments