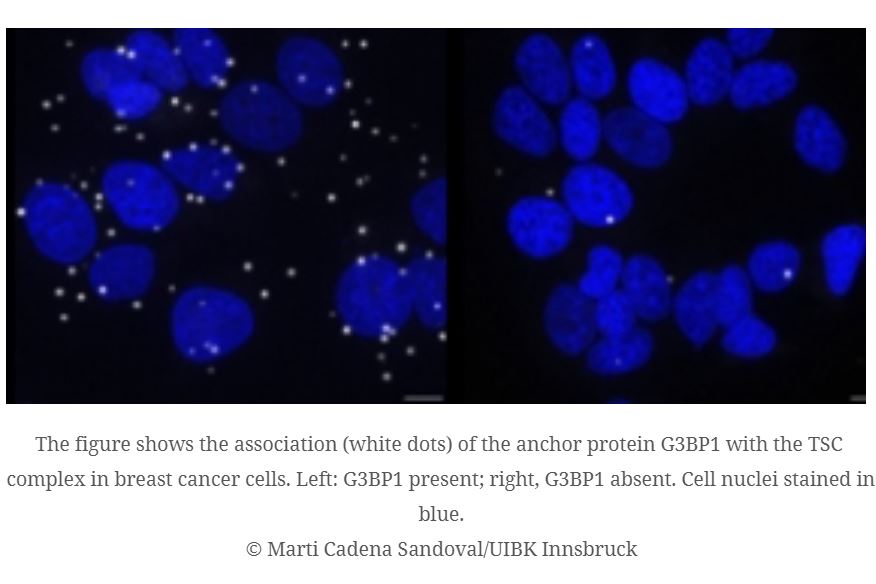
Certain anchor proteins inhibit a key metabolic driver that plays an important role in cancer and developmental brain disorders. Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the University of Innsbruck, together with a Europe-wide research network, discovered this molecular mechanism, which could open up new opportunities for personalized therapies for cancer and neuronal diseases. They published their results in the journal Cell.
The signaling protein MTOR (Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin) is a sensor for nutrients such as amino acids and sugars. When sufficient nutrients are available, MTOR boosts metabolism and ensures that sufficient energy and cellular building blocks are available...
Read More







Recent Comments