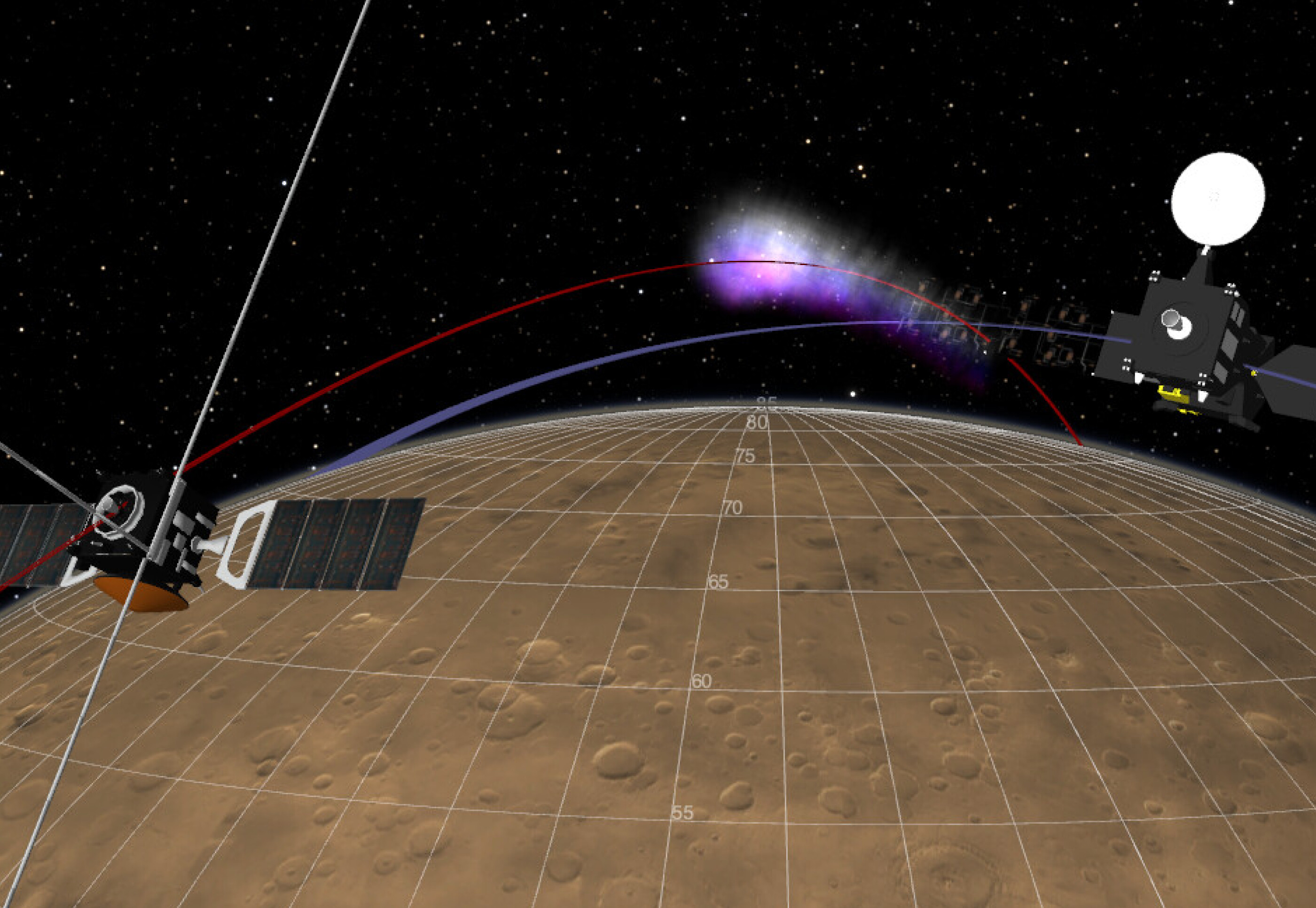
Using the repurposed equipment, a team including Imperial College London researchers have measured parts of the Martian atmosphere that were previously impossible to probe. This includes areas that can block radio signals if not properly accounted for—crucial for future Mars habitation missions.
The results of the first 83 measurements, analyzed by Imperial researchers and European Space Agency (ESA) colleagues across Europe, are published today in the journal Radio Science.
To achieve this, ExoMars’ Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) teamed up with another ESA spacecraft orbiting the red planet: Mars Express (MEX). The two craft maintain a radio link, so that as one passes behind the planet, radio waves cut through the deeper layers of the Martian atmosphere.
Changes in the atmospher...
Read More





Recent Comments