
Researchers at the University of Notre Dame have developed a novel, automated device capable of diagnosing glioblastoma, a fast-growing and incurable brain cancer, in less than an hour. The average glioblastoma patient survives 12–18 months after diagnosis.
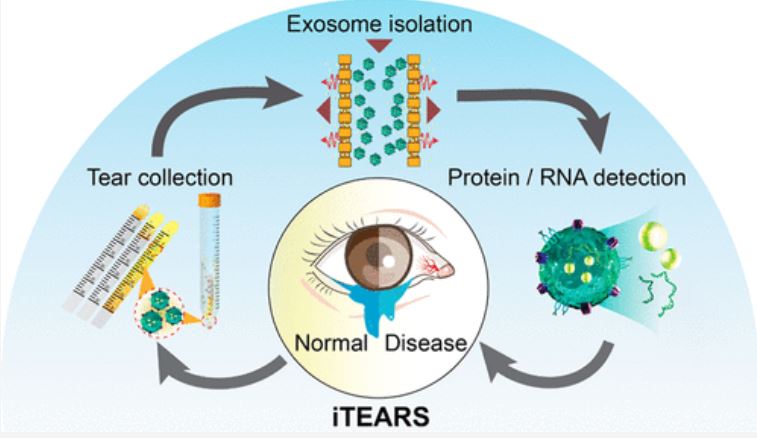
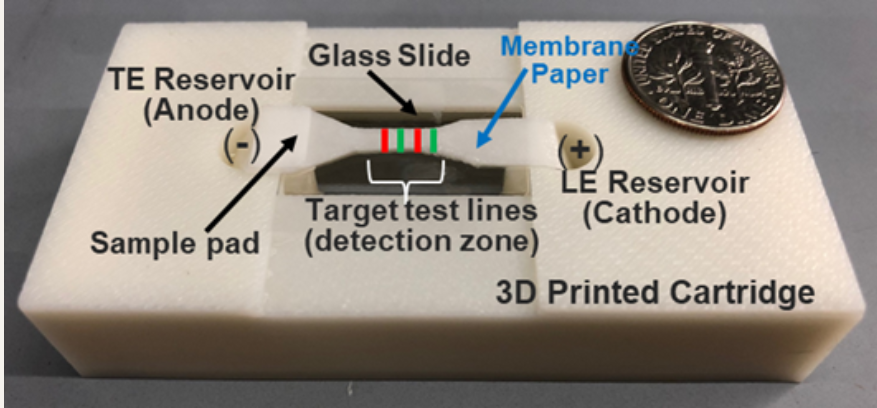
The crux of the diagnostic is a biochip that uses electrokinetic technology to detect biomarkers, or active Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors (EGFRs), which are overexpressed in certain cancers such as glioblastoma and found in extracellular vesicles.
“Extracellular vesicles or exosomes are unique nanoparticles secreted by cells...
Read More





Recent Comments