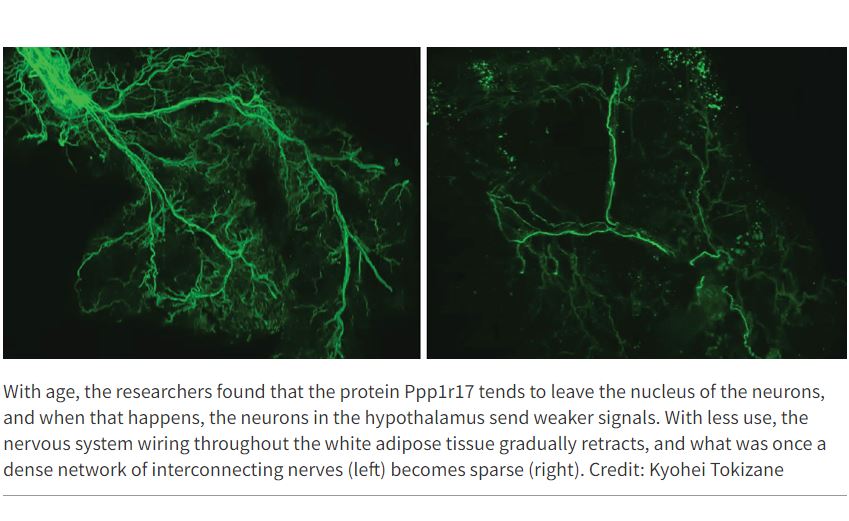
In recent years, research has begun to reveal that the lines of communication between the body’s organs are key regulators of aging. When these lines are open, the body’s organs and systems work well together. But with age, communication lines deteriorate, and organs don’t get the molecular and electrical messages they need to function properly.
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis identifies, in mice, a critical communication pathway connecting the brain and the body’s fat tissue in a feedback loop that appears central to energy production throughout the body. The research suggests that the gradual deterioration of this feedback loop contributes to the increasing health problems that are typical of natural aging.
The study—published in the jour...
Read More







Recent Comments