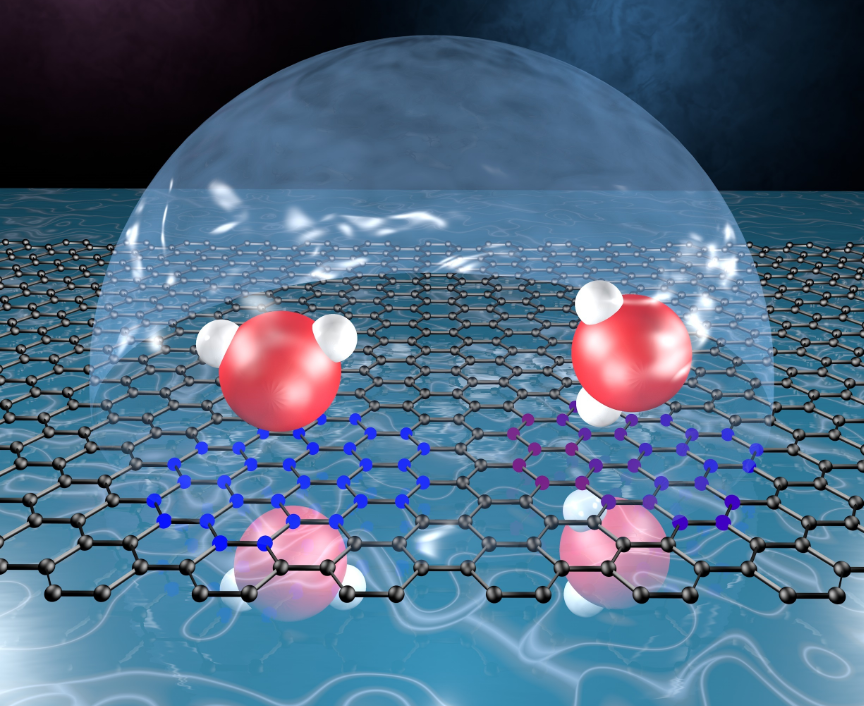
A recently published study led by Virginia Commonwealth University researchers sheds new light on how water interacts with the nanomaterial graphene, a single, thin layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice.
The researchers’ findings could hold implications for a variety of applications, including sensors, fuel cell membranes, water filtration, and graphene-based electrode materials in high-performance supercapacitors.
The study, “Solvent–Solvent Correlations across Graphene: The Effect of Image Charges,” was published in the American Chemica...
Read More





Recent Comments