
Credit: NASA/Fermi/Fang et al. 2022
Astronomers have long sought the launch sites for some of the highest-energy protons in our galaxy...
Read More

Astronomers have long sought the launch sites for some of the highest-energy protons in our galaxy...
Read More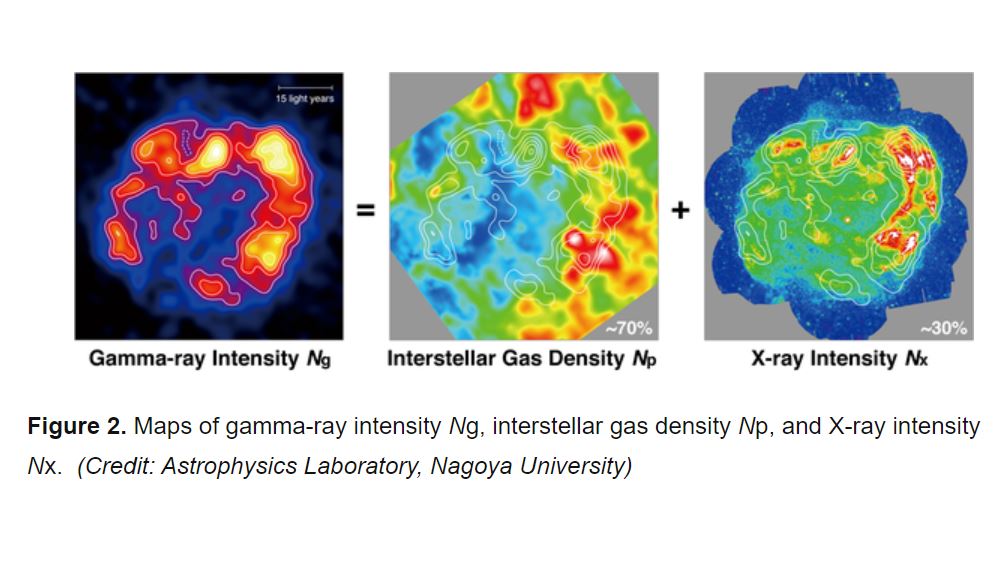
Astronomers have succeeded for the first time in quantifying the proton and electron components of cosmic rays in a supernova remnant. At least 70% of the very-high-energy gamma rays emitted from cosmic rays are due to relativistic protons, according to the novel imaging analysis of radio, X-ray, and gamma-ray radiation. The acceleration site of protons, the main components of cosmic rays, has been a 100-year mystery in modern astrophysics, this is the first time that the amount of cosmic rays being produced in a supernova remnant has been quantitatively shown and is an epoch-making step in the elucidation of the origin of cosmic rays.
The origin of cosmic rays, the particles with the highest energy in the universe, has been a great mystery since their discovery in 1912...
Read More
Recent Comments