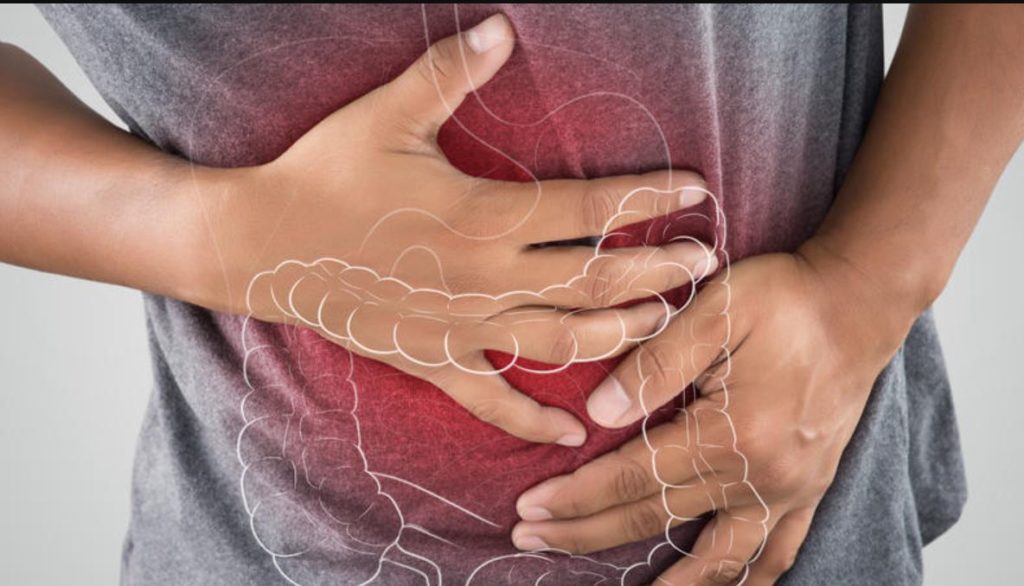
A team of researchers led by a biomedical scientist at the University of California, Riverside, has identified a novel mechanism by which loss-of-function mutations in the gene PTPN2, found in many patients with inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD, affect how intestinal epithelial cells maintain a barrier.
The intestinal epithelium, a single layer of cells, plays a critical role in human health by providing a barrier while also allowing nutrient and water absorption. Intestinal epithelial cells are needed for regulating immune function, communicating with the intestinal microbiota, and protecting the gut from pathogen infection – all of which critically depend on an intact epithelial barrier.
Affecting roughly 3 million Americans, IBD is a set of chronic intestinal diseases in wh...
Read More




Recent Comments