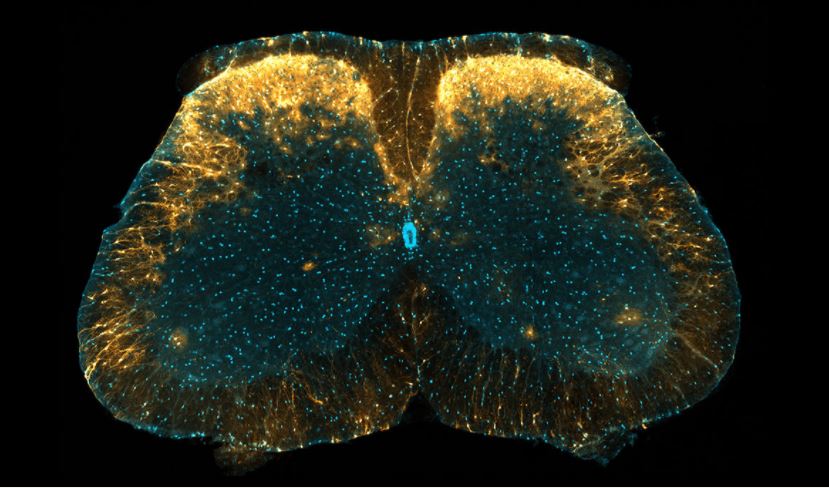
Researchers in Japan have revealed a previously unknown mechanism for pain control involving a newly identified group of cells in the spinal cord, offering a potential target for enhancing the therapeutic effect of drugs for chronic pain.
While neurons may be the most well-known cells of the central nervous system, an assortment of non-neuronal cells first discovered in the mid-nineteenth century also play a wide variety of important roles.
Originally named after the Greek word for “glue,” these glial cells are now known to be much more than glue and in fact are critical elements for regulating neuronal development a...
Read More







Recent Comments