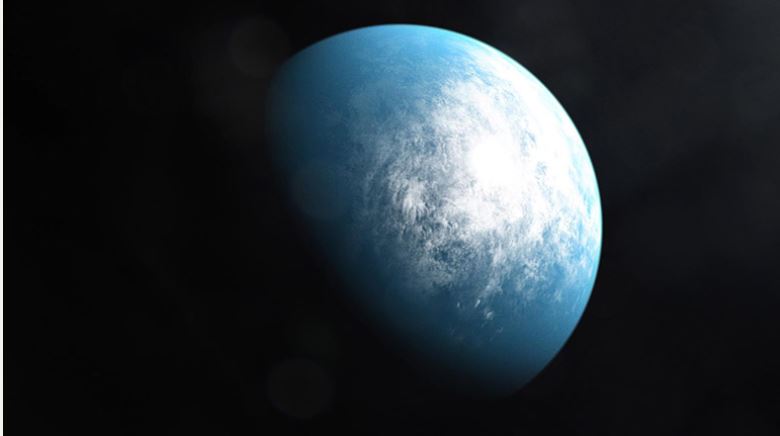

Findings will help better identify Earth-like planets that could sustain life. Astronomers have identified more than 4,000, and counting, confirmed exoplanets – planets orbiting stars other than the sun – but only a fraction have the potential to sustain life.
Now, new research from UBC’s Okanagan campus is using the geology of early planet formation to help identify those that may be capable of supporting life.
“The discovery of any planet is pretty exciting, but almost everyone wants to know if there are smaller Earth-like planets with iron cores,” says Dr...
Read More






Recent Comments