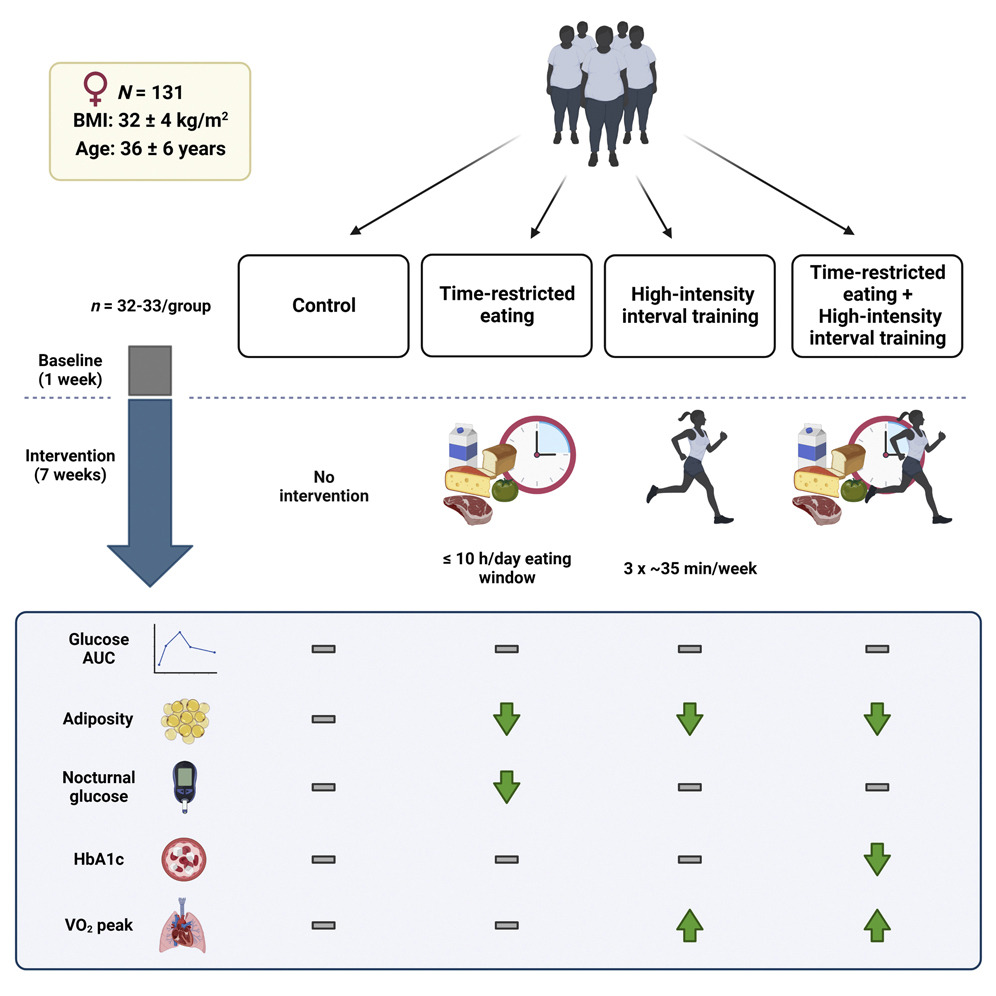
Both time-restricted eating (TRE) and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) have been shown to improve cardiometabolic health in people who are overweight and at risk of serious disease. Now a randomized, controlled trial has tested whether combining these two approaches is more effective than either of them on their own. The results, publishing in the journal Cell Metabolism on October 4, show that the combination improved the average long-term glycemic control compared to a no-intervention control group and induced 2-fold greater reductions in fat mass and visceral fat area compared with each intervention in isolation.
“Isolated TRE and HIIT have received increasing attention for being effective and feasible strategies for at-risk populations,” says senior author Trine Moholdt,...
Read More







Recent Comments