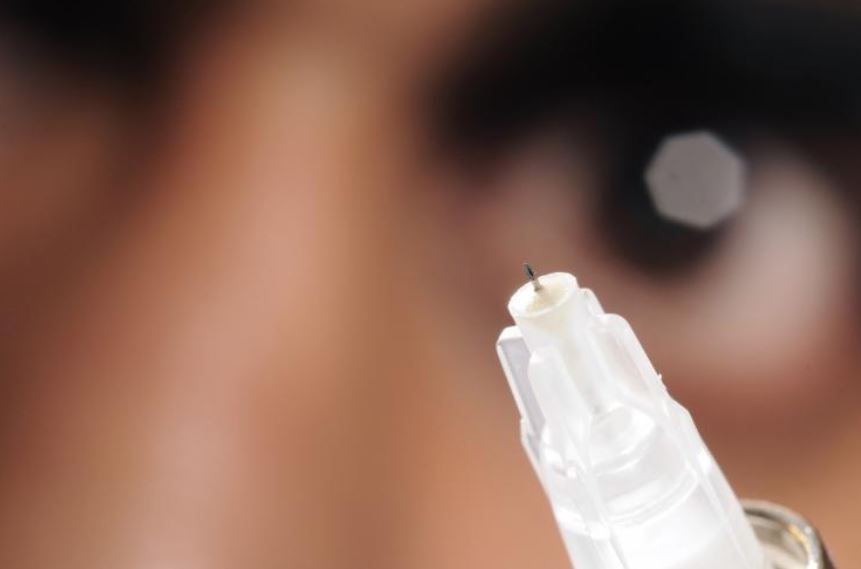

Researchers have developed a potential new treatment for the eye disease glaucoma that could replace daily eye drops and surgery with a twice-a-year injection to control the buildup of pressure in the eye. The researchers envision the injection being done as an office procedure that could be part of regular patient visits.
The possible treatment, which could become the first non-drug, non-surgical, long-acting therapy for glaucoma, uses the injection of a natural and biodegradable material to create a viscous hydrogel — a wa...
Read More






Recent Comments