
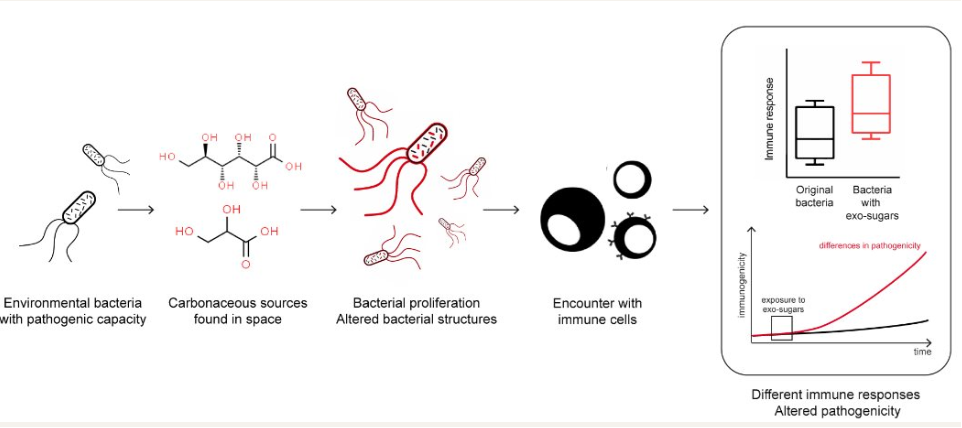
An inflammatory autoimmune response within the central nervous system similar to one linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS) has also been found in the spinal fluid of healthy people, according to a new Yale-led study comparing immune system cells in the spinal fluid of MS patients and healthy subjects. The research, published Sept. 18 in the journal Science Immunology, suggests these immune cells may play a role other than protecting against microbial invaders—protecting our mental health.
The results buttress an emerging theory that gamma interferons, a type of immune cell that helps induce and modulate a variety of immune system responses, may also play a role in preventing depression in healthy people.
“We were surprised tha...
Read More





Recent Comments