New study shows there may be a way to help even more psoriasis patients. About 7.5 million Americans suffer from psoriasis, an autoimmune disease that shows up as patches of red, inflamed skin and painful, scaly rashes. Although there are effective treatments for psoriasis, not everyone responds to these therapies — and for many, the relief is temporary.
“These therapies don’t reduce disease by 100 percent, and they don’t cure the disease” says La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) Professor Michael Croft, Ph.D. “And if you take patients off those drugs, the disease almost always comes back.”
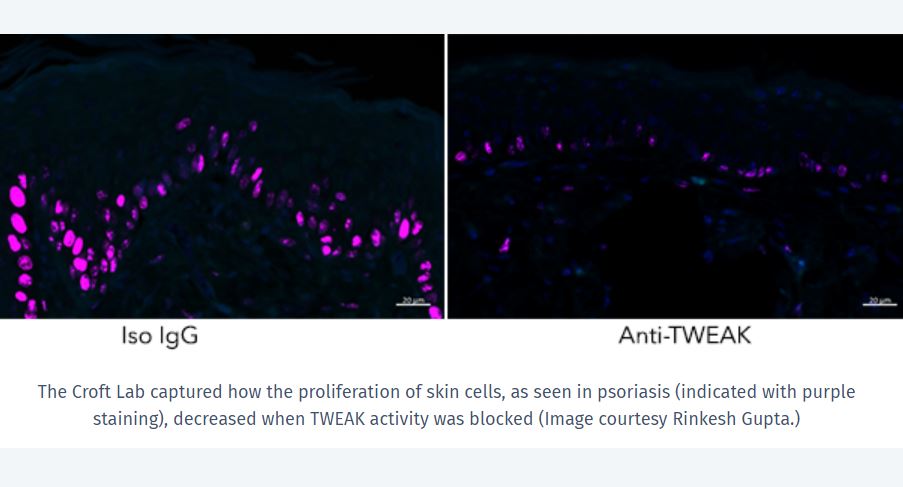
Now Croft and his team in LJI’s Center for Autoimmunity and Inflammation have discovered how a key protein called TWEAK damages skin cells in psoriasis patients...
Read More







Recent Comments