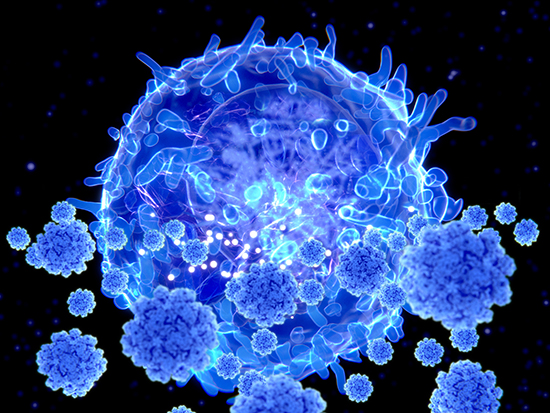
CD8+ T cells – known as “killer” T cells – are the assassins of the immune system. Once they are primed, they seek out and destroy other cells that are infected with virus or cells that are cancerous.
Priming involves dendritic cells – sentinels of the immune system. In an influenza infection in the lungs, for example, lung-migratory dendritic cells capture a piece of the viral antigen, and then migrate out of the lung to the place where naïve T cells reside, to present that antigen to the CD8+ T cells. This primes the T cells to know which cells to attack.
...Read More





Recent Comments