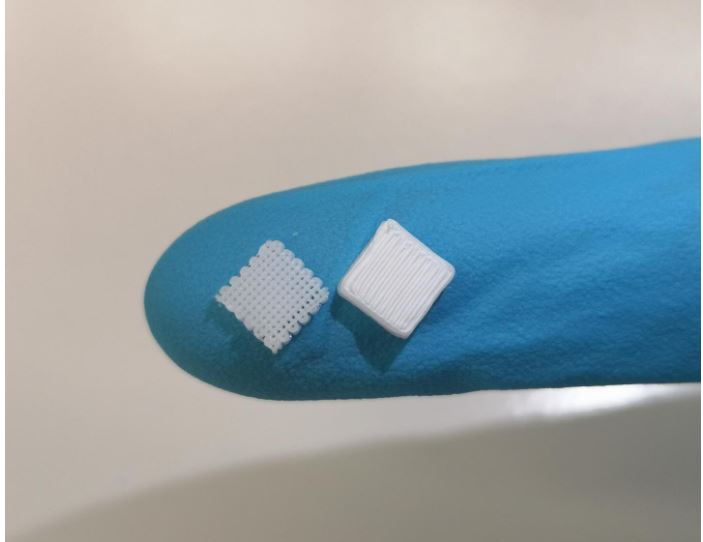
Chemists at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) have developed a way to integrate liquids directly into materials during the 3D printing process. This allows, for example, active medical agents to be incorporated into pharmaceutical products or luminous liquids to be integrated into materials, which allow monitoring of damage. The study was published in “Advanced Materials Technologies”.
3D printing is now widely used for a range of applications. Generally, however, the method is limited to materials which are liquefied through heat and become solid after printing...
Read More




Recent Comments