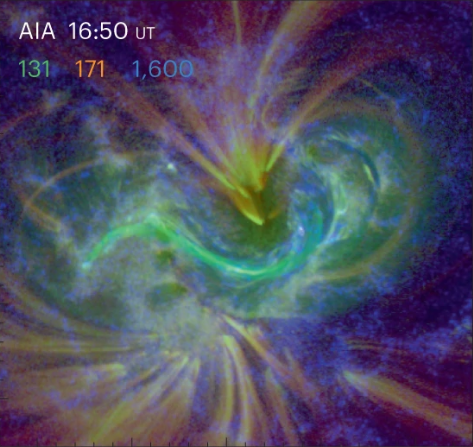
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Gou Yanyu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found that the solar outburst structure undergoes a complex reconfiguration evolution during the early outbursts. This is an important advancement in the study of solar outburst activity. This study was published in Nature Astronomy.
In classical images, the core structure of a solar eruption is a magnetic rope consisting of spirally wound magnetic lines. When the eruption begins, the magnetic ropes around the core are transformed by magnetic reconnection into spirally wound magnetic lines, which wrap around the original core, leading to its rapid growth in a “snowball” fashion...
Read More






Recent Comments