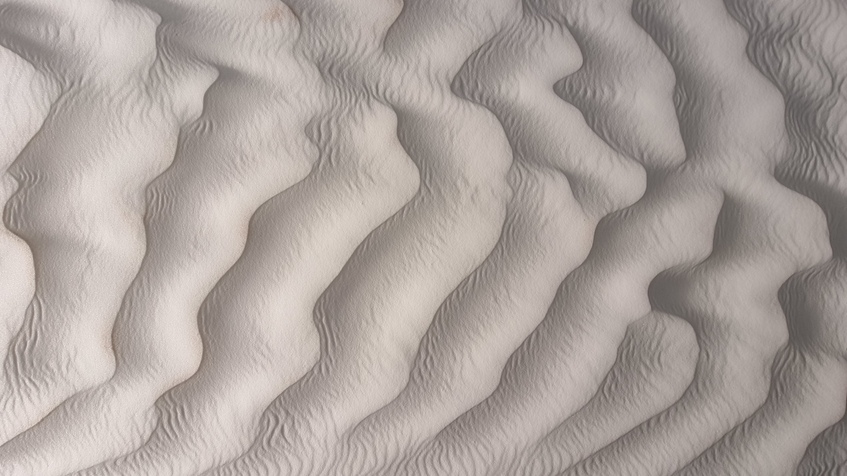

Small waves with a wavelength of centimeters and large waves with a wavelength of about 10 centimeters resemble waves due to the flow of water. The existence of two scales of waves on Mars was discovered by the Mars Curiosity Rover.| Photo: Hezi Yizhaq
Sand ripples are fascinating. They are symmetrical, yet wind — which causes them — is very much not. Furthermore, they can be found on Mars and on Earth. They would be even more fascinating if the same effect found on Mars could be found here on Earth as well. What if one unified theory could explain their formation on two different planets of our solar system?
Read More





Recent Comments