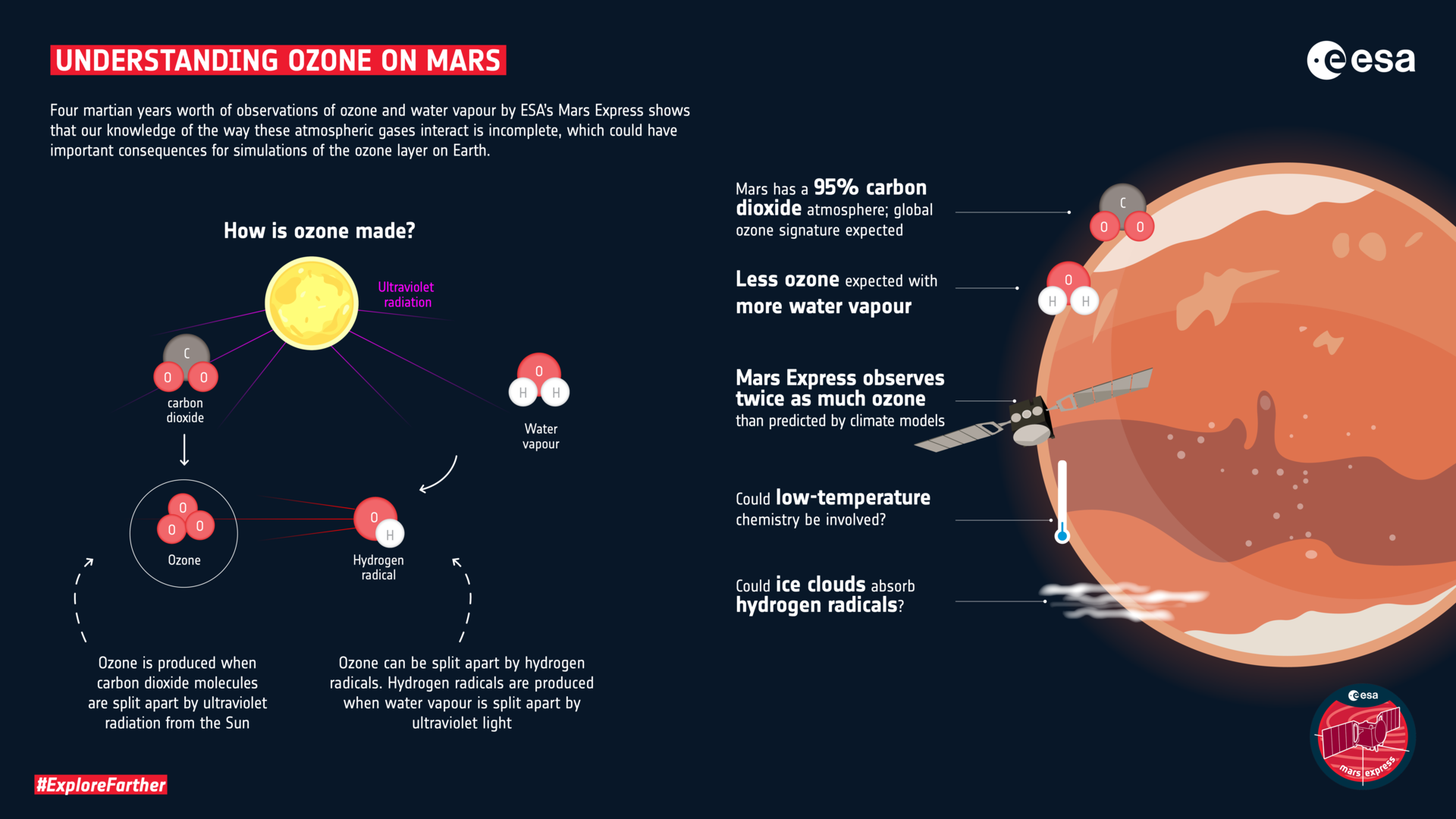
Long-term studies of ozone and water vapor in the atmosphere of Mars could lead to better understanding of atmospheric chemistry for the Earth. A new analysis of data from ESA’s Mars Express mission has revealed that our knowledge of the way these atmospheric gases interact with each other is incomplete.
Using four martian years of observations from the SPICAM (Spectroscopy for the Investigation of the Characteristics of the Atmosphere of Mars) instrument, which corresponds to seven and a half Earth years, a team of researchers from Europe and Russia uncovered the gap in our knowledge when trying to reproduce their data with a global climate model of Mars.
Ozone and water vapor do not make good atmospheric companions...
Read More







Recent Comments