
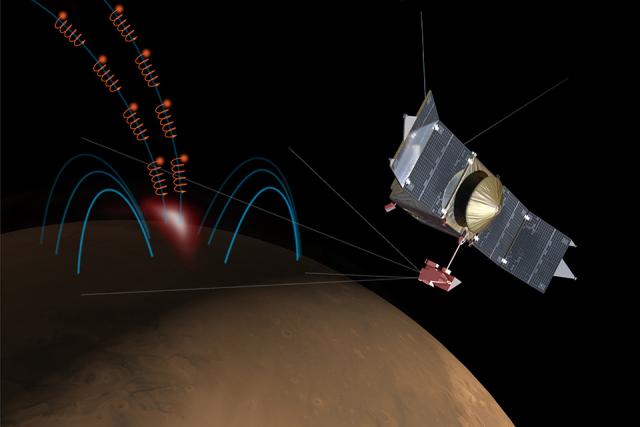
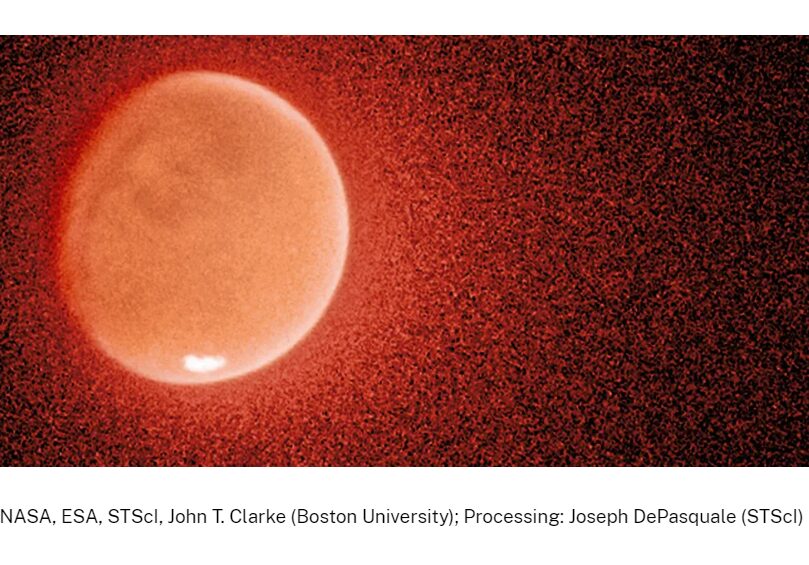
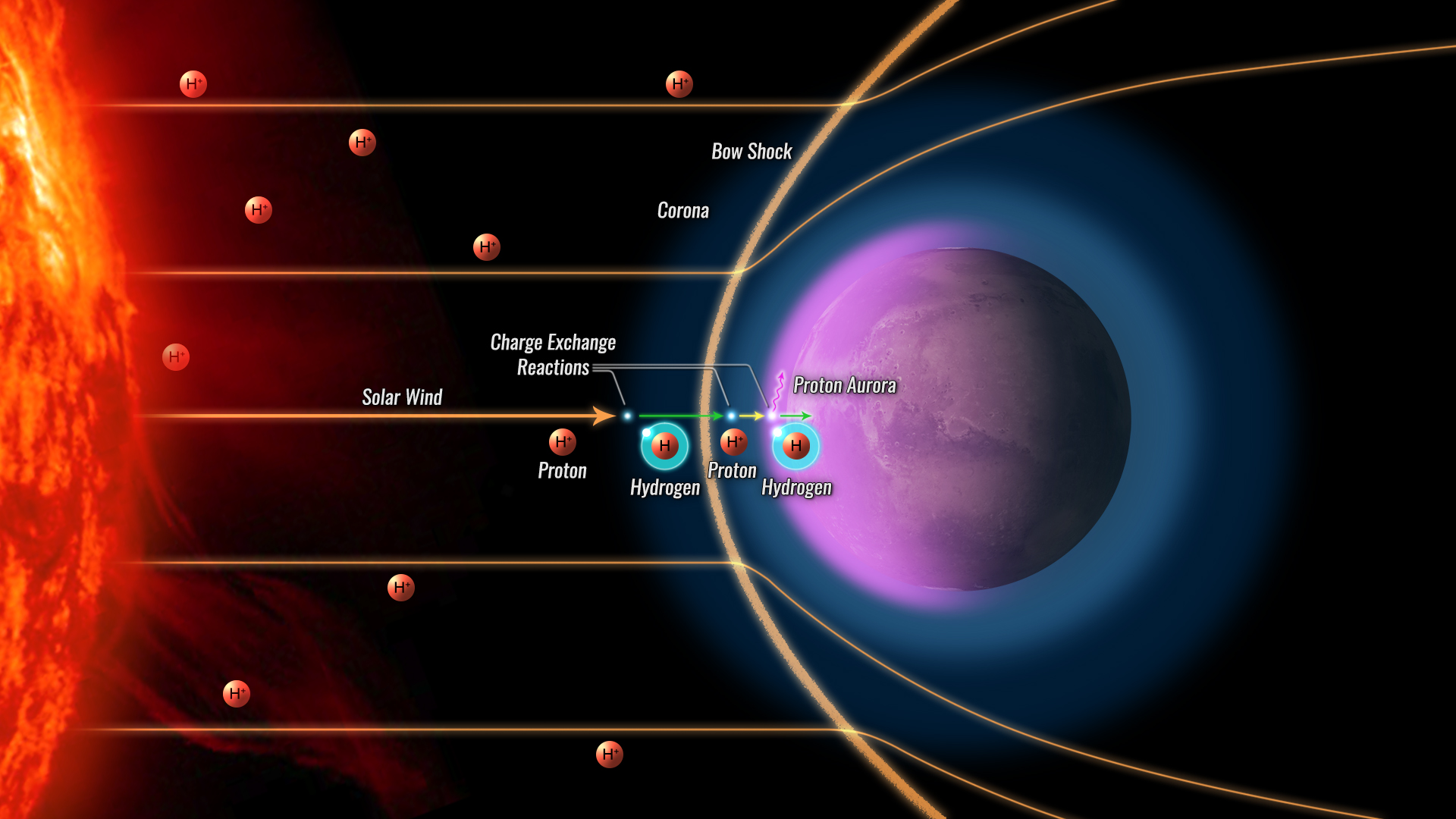
Mars’s atmosphere and climate are impacted by interactions with solar wind, a stream of plasma comprised of protons and electrons that flows from the sun’s outermost atmosphere (corona), traveling at speeds of 400–1,000 kilometers per second.
As these charged particles interact with the planet’s magnetic field and atmosphere, we may see spectacular auroras over polar regions on Earth. Given Mars’s lack of a global magnetic field, auroras here are instead diffused across the planet.
However, sometimes this solar wind can “disappear” in rare events when there is a gap in the solar wind path as the sun increases its solar activity...
Read More





Recent Comments